5G home internet offers a faster, more affordable alternative to satellite for many rural households, though availability remains the biggest hurdle.
Key Takeaways
- 5G home internet is generally cheaper and has lower latency than traditional satellite internet, making it better for gaming and video calls.
- Satellite internet offers wider coverage, serving remote areas where 5G towers haven’t reached yet.
- Starlink is the exception, offering speeds and latency closer to 5G but at a significantly higher equipment and monthly cost.
Few things are more frustrating during the process of moving to a rural or semi-rural home than realizing fiber and cable internet aren’t available at your new address. You are often left staring at two confusing wireless options: 5G home internet and satellite. It can feel like choosing between the lesser of two evils, but the technology has improved significantly in recent years. This guide compares both services based on speed, budget, and lifestyle needs to help you make the right connection.
The Core Difference: How the Signals Reach Your Home
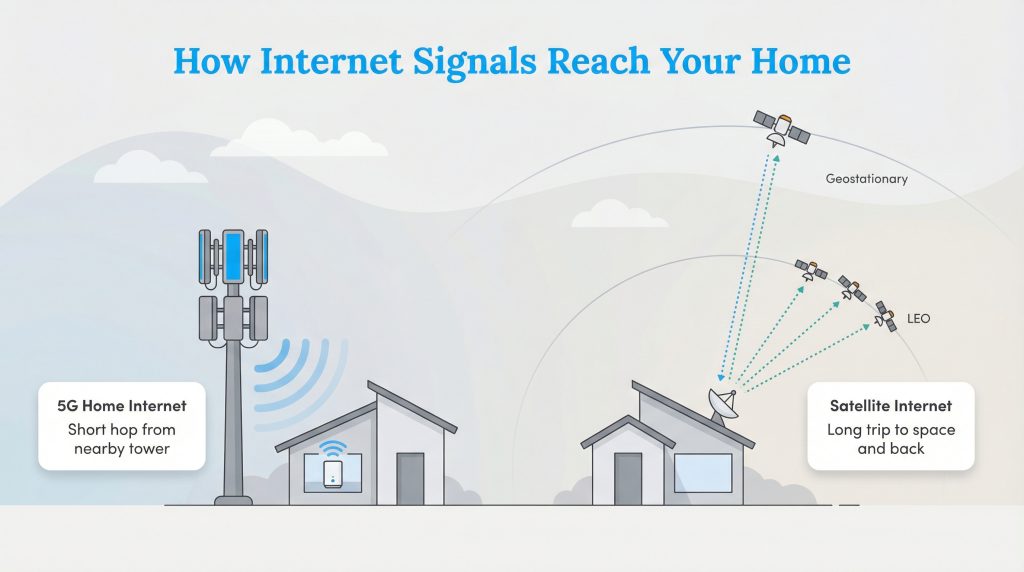
To understand the difference between these two services, it helps to visualize the “pipeline” that delivers data to your house.
5G Home Internet uses the same cellular towers that connect your smartphone. When you browse the web, the signal takes a short wireless hop from a nearby tower to the gateway box sitting in your window. Because the tower is local, usually within a few miles, the data travels quickly.
Satellite Internet beams your data from a dish on your roof all the way up to space and back. Traditional satellite providers like Viasat and HughesNet use geostationary satellites that orbit 22,000 miles away, creating a very long pipeline. Newer options like Starlink use Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites, which sit much closer to Earth, significantly shortening the travel time but still requiring a clear view of the sky.
At a Glance: 5G Home vs. Satellite Comparison Table

Here is a breakdown of how the average specifications compare across the three main categories of wireless internet.
| Feature | 5G Home Internet | Traditional Satellite (HughesNet/Viasat) | Starlink (LEO Satellite) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Typical Download Speed Range | 50–300 Mbps | 25–100 Mbps | 50–200+ Mbps |
| Latency (Ping) | 30–60 ms | 600 ms+ | 25–50 ms |
| Typical Monthly Cost | $50–$60 | $65–$150 | $120+ |
| Data Caps | Usually Unlimited | Strict Caps | Unlimited / Priority |
| Installation | Self-install (Plug & Play) | Pro install required | Self-install (Roof/Dish) |
Speed and Latency: Why It Matters for Gaming and Work
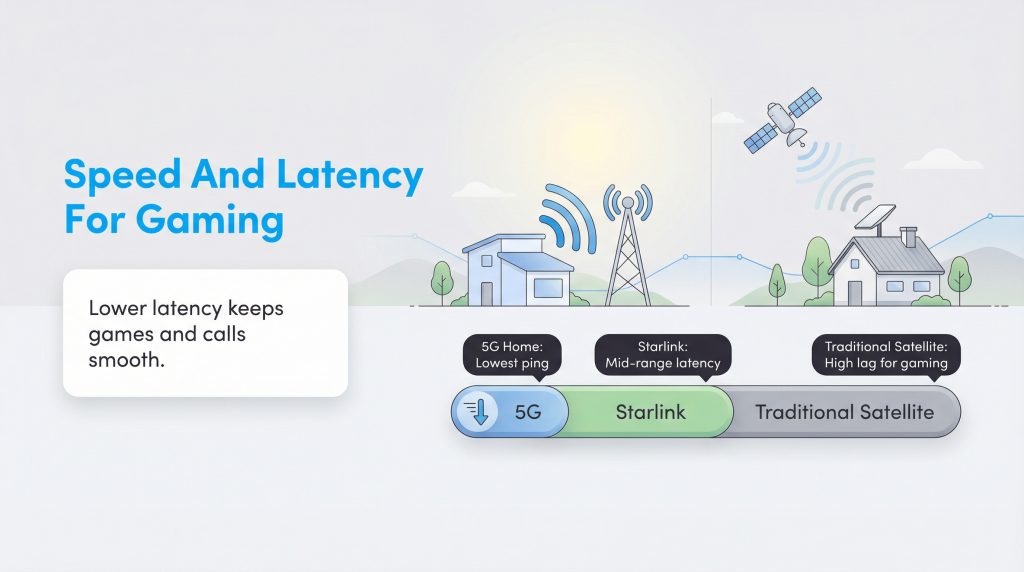
When comparing 5G home internet vs. satellite internet speed, raw numbers don’t tell the whole story. 5G speeds can fluctuate heavily depending on how close you are to the tower and how many people are using the network. However, you can generally expect speeds fast enough for 4K streaming and multiple devices. Traditional satellite is consistently slower, often struggling to support more than one heavy user at a time.
There is a major nuance here: Starlink vs. 5G home internet. Starlink is the only satellite provider that truly competes with 5G on speed. In many rural areas, Starlink actually outperforms 5G download speeds, especially if you live on the edge of a cell tower’s range. However, 5G networks in suburban areas or near highways can easily surpass Starlink’s averages of 50–200 Mbps.
The biggest factor for working from home or gaming is latency (or ping). This is the time it takes for a signal to travel from your computer to the server and back. Because traditional satellite signals must travel 22,000 miles into space, they have massive latency (600ms+), making Zoom calls laggy and real-time online gaming impossible. In the battle of satellite vs. 5G internet for gaming, 5G is the clear winner because the signal stays local. Starlink has solved much of this issue, but 5G generally offers a more stable ping for competitive gaming. Even when speeds are similar, latency on 5G is typically lower and more stable, which matters more for most online games.
If you aren’t sure what performance metrics your household requires, check out our guide on how much internet speed you really need.
Cost Comparison: Monthly Fees and Hidden Expenses

If your primary concern is your budget, the cost of 5G home internet vs. satellite usually favors 5G by a wide margin. 5G plans are typically simple, many costing around $50–$60 per month. These plans rarely have contracts or data caps, meaning your bill stays predictable.
Satellite internet is almost always more expensive. Traditional plans often start around $65 but can climb over $150 if you want decent speeds and more data. Furthermore, satellite providers often require two-year contracts, with steep early termination fees if you cancel.
Equipment costs are another major differentiator. Most 5G providers include the gateway box for free or a nominal rental fee. In contrast, Starlink requires you to purchase the hardware upfront, which typically costs around $599 to start. Traditional satellite providers may lease the equipment to you, but that adds another $15 or $20 to your monthly bill.
Installation: Plug-and-Play vs. Drilling Holes
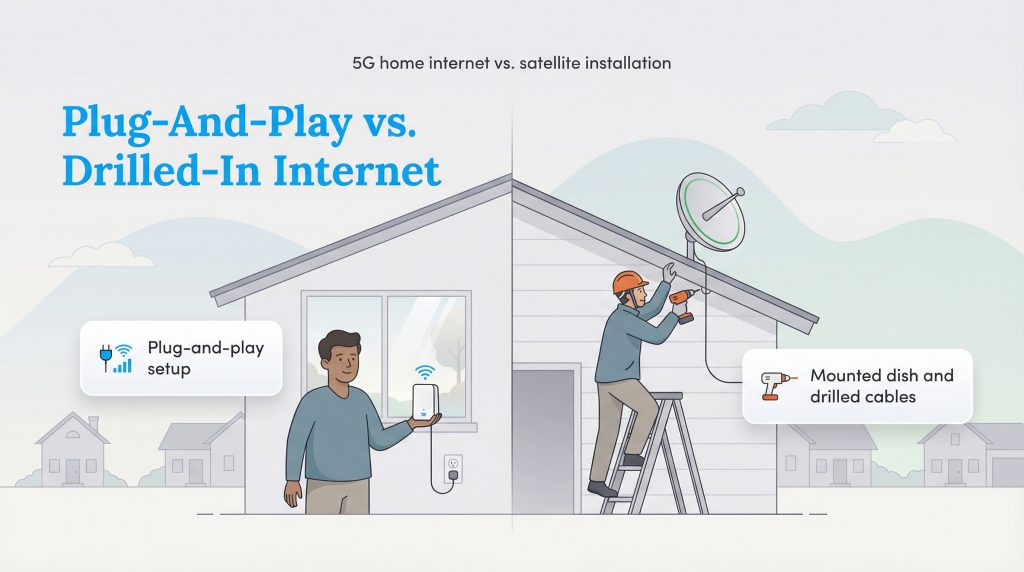
For renters or anyone who dislikes DIY projects, 5G home internet is the clear winner regarding installation. The “installation” process usually involves unboxing a gateway device, plugging it into a standard wall outlet, and placing it near a window with a good signal. It is completely non-invasive, making it one of the easiest internet options for rural areas in 2026. If you move, you simply unplug the box and take it with you.
Satellite internet requires a much more complex setup. To get a reliable signal, a satellite dish must be mounted on your roof or a pole with a completely unobstructed view of the sky. This often involves climbing ladders, drilling holes in your siding or roof shingles, and running cables through walls. Traditional providers usually send a professional technician to handle this, but you still have to deal with the permanent hardware on your home. Starlink is a DIY installation, but it still requires physical mounting and cable routing, which can be difficult or dangerous depending on your home’s architecture.
Reliability: Weather Impact and Network Congestion
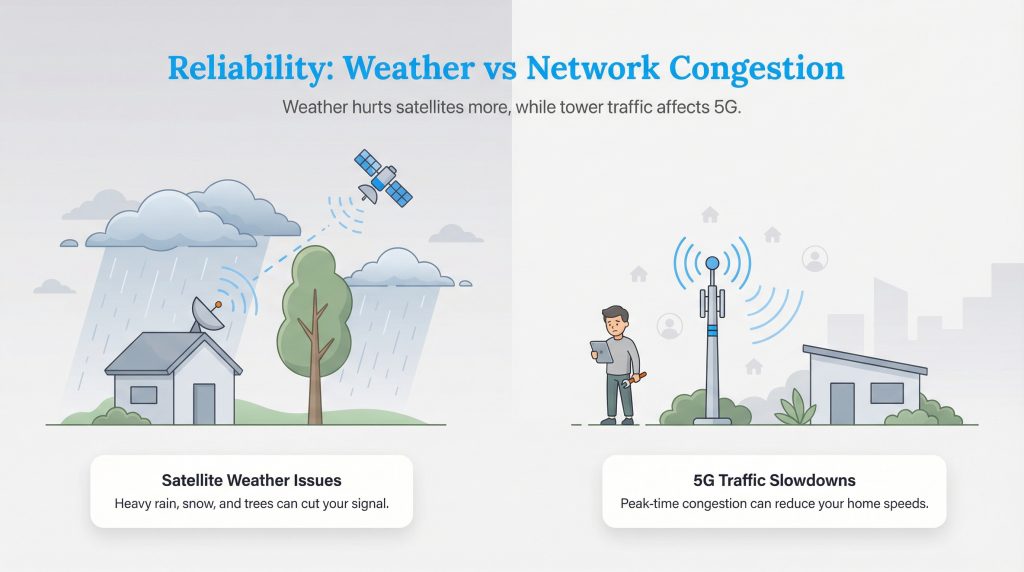
Reliability of 5G vs. satellite internet often comes down to two factors: weather and traffic.
Satellite internet is notorious for “rain fade.” Because the signal has to travel through the entire atmosphere, heavy rain, snow, or thick cloud cover can scatter the signal and cut off your connection entirely. While severe storms can affect any wireless signal, satellite users in areas with frequent storms often find this a major frustration.
5G internet is much more resistant to weather, as the signal travels a shorter distance near the ground. In dense urban environments, buildings can obstruct 5G, but in rural areas, the signal is generally reliable. However, 5G suffers from “deprioritization.” Cellular networks prioritize mobile phone traffic over home internet traffic. This means that during peak hours, like 7 p.m. when everyone is streaming video, your home internet speeds might suddenly drop if the local tower gets congested.
It is also worth noting that Starlink requires a completely clear field of view. Even a single tree or tall structure blocking the path of the satellite can cause frequent service interruptions, known as obstructions.
The Eco-Conscious Choice: Energy and Hardware
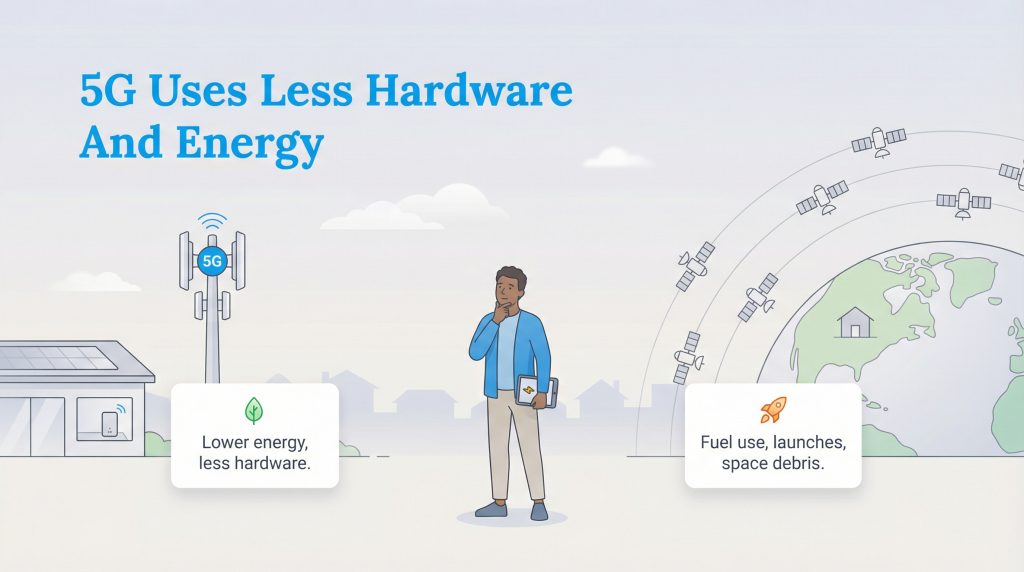
When considering sustainable living, 5G home internet has a smaller environmental footprint. It utilizes existing cell tower infrastructure, meaning no new major construction is needed to connect your home. The equipment is a small, all-in-one plastic gateway that consumes relatively little power.
Satellite constellations, particularly LEO networks like Starlink, require frequent rocket launches to maintain thousands of satellites in orbit. These launches consume significant fuel and resources and contribute to the growing problem of orbital debris, or “space junk.” Additionally, satellite dishes are large, metal-and-plastic assemblies that use more raw materials than simple 5G gateways. You can read more about the challenges of orbital debris from NASA’s resources on space debris to understand the broader impact of space-based infrastructure.
The Verdict: Which Internet Type is Right for You?

Choosing between these two technologies largely depends on your location and your lifestyle. We recommend running a coverage check for 5G home internet first. If it is available, it is almost always the better value. If not, look into LEO satellite options like Starlink before settling for traditional satellite providers.
Here is a quick summary of the winners by category:
| Use Case | Best Option | Why? |
|---|---|---|
| Gamers & Remote Workers | 5G Home Internet | Lower, more stable latency prevents lag. |
| Deep Rural Living | Satellite (Starlink) | Works where cell towers don’t reach, provided you have a clear sky view. |
| Renters | 5G Home Internet | No holes to drill and easy to move to a new apartment. |
| Tight Budget | 5G Home Internet | Much lower monthly cost and $0 equipment fees. |
FAQs About 5G and Satellite Internet
Is 5G home internet faster than Starlink?
Can I use satellite internet for gaming?
Do I need a phone line for 5G home internet?
Does weather affect 5G internet like it does satellite?
Which is cheaper: 5G or satellite?
About the Author
LaLeesha has a Masters degree in English and enjoys writing whenever she has the chance. She is passionate about gardening, reducing her carbon footprint, and protecting the environment.
