Understanding where your power comes from helps you make smarter, more sustainable choices for your household.
Key Takeaways
- Renewable electricity is generated from natural sources that replenish themselves, such as sunlight, wind, and water.
- The power grid works like a giant pool where renewable and non-renewable electrons mix together before reaching your home.
- Choosing a green energy plan encourages more renewable generation, even if the specific electrons powering your lights aren’t exclusively “green.”
Have you ever looked at your electric bill or browsed a new utility plan and wondered what terms like “100% Wind” or “Green Mix” actually mean for your home? While most of us know that solar panels and wind turbines exist, understanding how that energy transforms into the electricity coming out of your outlets can be confusing. The reality of the power grid is fascinating and slightly complex, but knowing how it works is the first step toward lowering your carbon footprint and potentially stabilizing your monthly bills. This guide will walk you through exactly what renewable electricity is, how it differs from the broader concept of renewable energy, and what really happens when you sign up for a green power plan.
What Is Renewable Electricity?
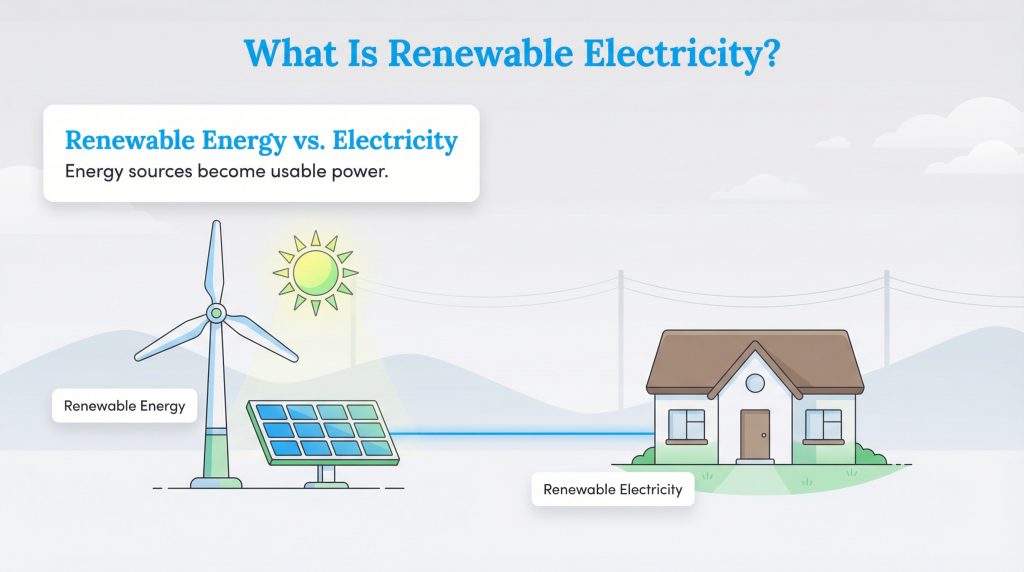
To put it simply, renewable electricity is electricity produced by energy sources that naturally replenish themselves on a human timescale. Unlike fossil fuels like coal or natural gas, which take millions of years to form and are finite, sources like wind and sunlight are constantly available. This endless supply is why they are key to a sustainable future.
It is helpful to understand the difference between renewable energy vs. renewable electricity. “Renewable energy” is the broad term for the source itself, the kinetic energy in the wind, the heat from the earth, or the radiation from the sun. This energy can be used for many things, such as heating water or fueling vehicles. “Renewable electricity,” however, is the specific product created when we capture that energy and turn it into the electrical current that powers your toaster, TV, and lights. That distinction matters when you’re comparing electricity plans, because you’re not choosing a fuel source directly, you’re choosing how much of your power bill supports renewable generation. When you pay your utility bill, you are paying for this specific usable product delivered via wires, not the raw energy source itself.
How Renewable Electricity Reaches Your Home

One of the biggest misconceptions about signing up for a “green energy plan” is that green electrons will flow specifically to your house while your neighbor gets the dirty ones. The electrical grid doesn’t work that way. A great way to visualize how renewable electricity works on the grid is to think of it as a giant bathtub.
Imagine that all the power plants in your region, whether they burn coal, harness wind, or split atoms, are pouring water into this massive tub. Once the water (electricity) is in the tub (the grid), it all mixes together. You cannot separate the “clean water” from the “dirty water.” When you turn on your faucet (your lights), you get a mix of whatever is in the tub at that moment. This grid mix can change hourly based on demand and generation, but choosing renewables helps add more clean energy over time.
So, why bother choosing a renewable plan? When you pay for a green plan, you are effectively paying someone to pour more clean water into the tub. While the water coming out of your faucet is still a mix, your payment ensures the overall mixture becomes cleaner for everyone, reducing the need for dirty sources to fill the tub.
Types of Renewable Electricity Sources

There are several examples of renewable electricity sources we use to generate clean power today. While some are more common in certain regions than others, they all play a role in greening the grid.
- Solar Power: This technology uses photovoltaic cells to convert sunlight directly into electric current. You can learn more about how this works on our solar page.
- Wind Power: Large turbines capture the kinetic energy of moving air to spin a generator, creating electricity without any emissions.
- Hydropower: One of the oldest forms of electricity generation, hydropower uses the flow of water in rivers or dams to spin turbines.
- Geothermal: This method taps into the heat naturally stored beneath the earth’s surface to generate steam and drive turbines.
- Biomass: This involves burning organic materials like wood waste or agricultural crops. While renewable, it is sometimes debated regarding its total environmental impact compared to wind or solar.
What’s most common in your area will depend on local resources. In many parts of the U.S., wind and solar are the fastest-growing sources, while hydropower dominates in some regions with large rivers.
Renewable vs. Green vs. Clean Energy: What’s the Difference?

You will often hear terms like “green energy” and “clean energy” used interchangeably with renewable energy. While they are related, they have distinct meanings that are helpful to know when shopping for electricity plans.
| Term | Definition | Primary Example |
|---|---|---|
| Renewable | Energy from a source that naturally replenishes itself over a short period. | Wind, Biomass |
| Green | A marketing and policy term for energy sources that provide high environmental benefit, though specific criteria can vary. | Solar, Wind |
| Clean | Energy generation that produces very low greenhouse gas emissions during operation. | Nuclear, Solar |
For example, nuclear energy is “clean” because it releases zero carbon, but it isn’t “renewable” because uranium is a finite resource. Solar is often considered renewable, green, and clean because it relies on abundant sunlight and has very low emissions when operating.
The Benefits of Renewable Electricity

Switching to renewables isn’t just about feeling good; it has tangible benefits for our society and economy. The most obvious benefit is the environmental impact. By relying on wind and sun, we drastically reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution, leading to cleaner air and a healthier planet.
There is also the factor of energy independence. Renewable resources are domestic—the wind blows and the sun shines right here in the U.S., meaning we rely less on imported fossil fuels. Furthermore, renewables offer potential price stability. The “fuel” for a solar panel (sunlight) is free, which helps insulate the market from the volatile price spikes often seen with oil and natural gas. You can read more about the growth of these sources from the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA).
Is Renewable Electricity Cheaper?

Historically, eco-conscious consumers had to pay a steep premium to support green energy. However, the landscape has shifted dramatically. The technology costs for solar panels and wind turbines have plummeted, making them cheaper to build and operate than coal plants in many parts of the country.
That said, if you are looking at consumer electricity plans, you might still see a small price difference. Some “Green Plans” include a slight premium, often called a “Green Adder,” which covers the cost of purchasing Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) to verify the power’s origin. But this isn’t always the case.
Money-Saver: In deregulated markets like Texas or Pennsylvania, competitive renewable plans are sometimes cheaper than fossil-fuel plans, especially when natural gas prices are high, depending on current market conditions and plan terms. Always compare rates to see if you can save on your electric bill while going green.
How to Choose a Renewable Plan for Your Home
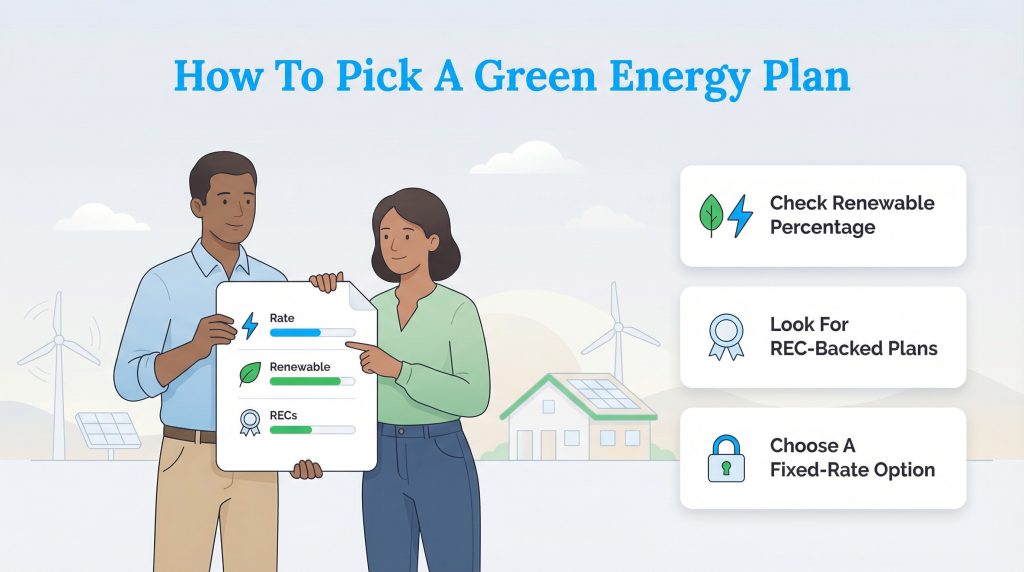
If you are ready to make the switch, the process is straightforward. In deregulated markets, you have the power to choose your provider. When comparing plans, look for the “Renewable Content” percentage on the Electricity Facts Label (EFL) or look for phrases like “100% renewable content” on the bill details. You want a plan that is backed by Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs). An REC is essentially a receipt that proves 1 megawatt-hour of electricity was generated from a renewable source and added to the grid on your behalf.
We recommend looking for fixed-rate green plans. These lock in your price per kilowatt-hour for the duration of your contract, protecting you from seasonal price spikes. If you live in a regulated market where you can’t choose your supplier, check your local utility’s website. Many offer “green power programs” that allow you to support renewable generation for a small monthly fee. For more help finding providers in your area, visit our electric service hub.
Learn more about Renewable Energy Plans
Why Switching To Renewable Electricity Is Easier Than Ever

Changing how you power your home is one of the most impactful steps you can take toward a sustainable lifestyle. You don’t need to install solar panels on your roof to make a difference; simply understanding the grid and choosing a provider that prioritizes renewable sources helps drive the demand for a cleaner future. As technology improves and costs continue to drop, renewable electricity is moving from a niche option to a mainstream choice. By staying informed and reviewing your options, you can enjoy reliable power while knowing you are doing your part for the planet.
FAQs About Renewable Electricity
How is renewable electricity generated?
What is the difference between renewable energy and renewable electricity?
Do I need special equipment to use renewable electricity?
Is renewable electricity reliable?
Can I get renewable electricity if I rent my home?
Why is green energy sometimes more expensive?
About the Author
LaLeesha has a Masters degree in English and enjoys writing whenever she has the chance. She is passionate about gardening, reducing her carbon footprint, and protecting the environment.
