High latency causes delays in data transmission, resulting in frozen video calls and gaming lag, even if you have a high-bandwidth internet plan.
Key Takeaways
- Latency is the time it takes for data to travel from your device to a server and back, often measured in milliseconds (ms).
- Bandwidth and latency are different, meaning you can have “fast” download speeds (bandwidth) but still experience lag if your latency is high.
- Switching to fiber internet or using a wired Ethernet connection are the most effective ways to lower latency and improve smart home performance.
Have you ever been on a crucial video call only for your face to freeze mid-sentence, or watched your character glitch in a video game right before a big win? It’s incredibly frustrating, especially when you’re paying for a “high-speed” internet plan that promised top-tier performance. Many people assume their internet speed is simply too slow, but the real culprit behind these delays is often not speed at all, it’s latency. While bandwidth determines how much data you can move, latency dictates how fast that data gets there. In this guide, we will help you understand what causes these lags and how you can troubleshoot your connection to get things running smoothly again.
What Is Latency in Simple Terms?
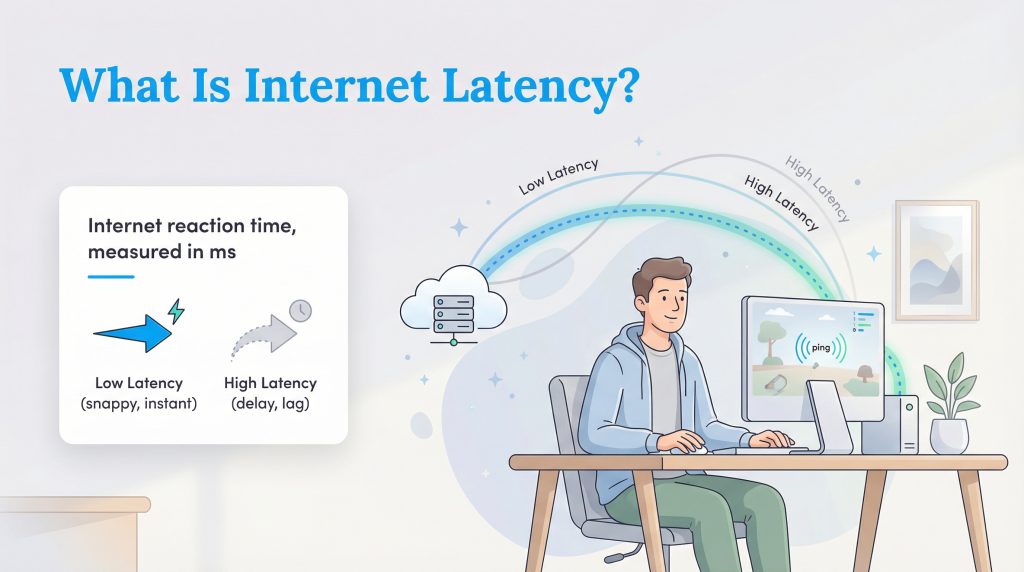
To put it simply, latency is the reaction time of your internet connection. Imagine you are playing a game of ping pong. Latency is the time it takes for the ball to be hit across the table and return to you. In the world of the internet, the “ball” is a packet of data sent from your computer to a website’s server and back again. If that trip takes a long time, you experience a delay.
This delay is measured in milliseconds (ms), and in gaming or speed test contexts, you will often hear it referred to as “ping.” The goal is always to have a low number here. Low latency means your connection has a fast reaction time, making everything feel snappy and instant. High latency, on the other hand, means a slow reaction time, resulting in that dreaded lag where your actions on screen happen a second or two after you press the button.
Latency vs. Bandwidth: Understanding the Difference
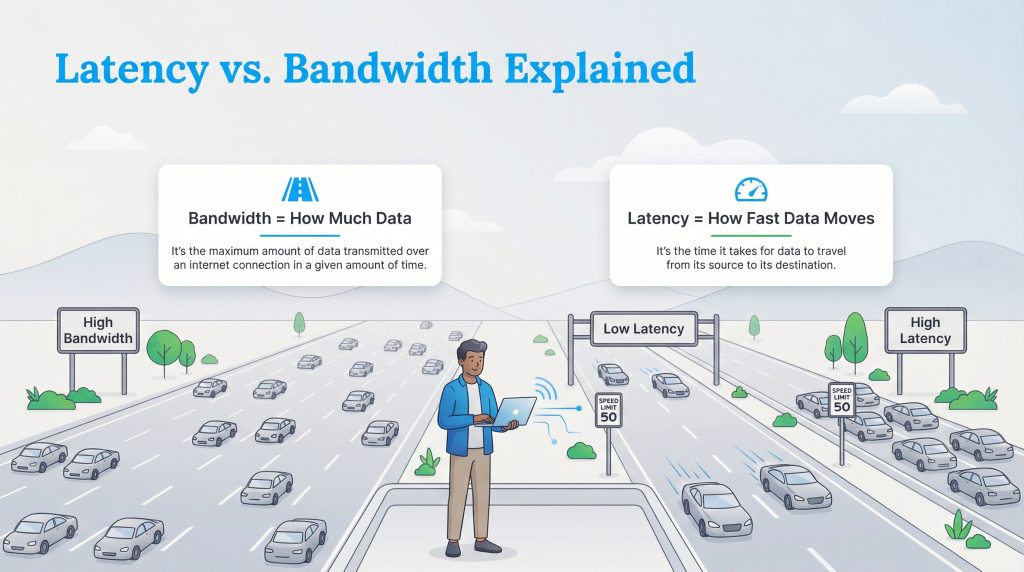
Confusion between these two terms is common, but understanding the difference is key to fixing your internet woes. The best way to visualize latency vs bandwidth is with a highway analogy.
Think of bandwidth as the number of lanes on a highway. If you have a massive 10-lane highway (High Bandwidth), you can fit a lot of cars on the road at once. This is great for downloading large files because you can move a lot of data simultaneously. However, latency is the speed limit or how fast those cars are actually driving. If that 10-lane highway has a speed limit of 5 mph (High Latency), it doesn’t matter how wide the road is; the cars, or your data, will still arrive late.
You can have the widest, most expensive highway in the world, but if the traffic is crawling, your experience will feel slow. This is why you can have a gigabit connection and still struggle with lag on Zoom calls. Bandwidth gives you capacity, but latency gives you responsiveness.
Learn more about What a Good Internet Speed Is
Why Low Latency Matters for Your Home
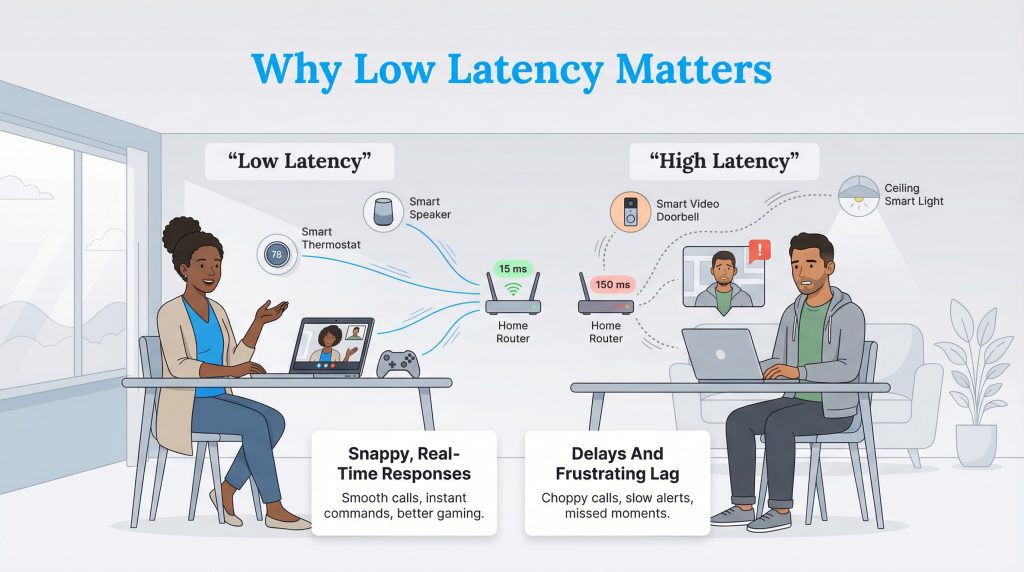
We often focus on download speeds when shopping for internet, but latency is what actually makes your digital life feel smooth. In a modern smart home, responsiveness is everything. If you have high latency, your smart video doorbell might take too long to notify you that someone is at the door, or your smart lights might hesitate before turning on after you issue a voice command. These small delays add up to a clunky, frustrating experience.
For those of us working from home, latency is even more critical. Applications like Zoom or Microsoft Teams rely on real-time communication. Unlike downloading a PDF, where a few seconds of delay doesn’t matter, a delay in a conversation leads to talking over one another and awkward pauses. If you use a VPN (Virtual Private Network) for work security, latency becomes even more noticeable because your data has to travel an extra step to the VPN server before reaching its destination. Of course, for gamers, split-second reaction times are the difference between winning and losing. You need your internet to react as fast as you do.
What Is a Good Latency Speed?
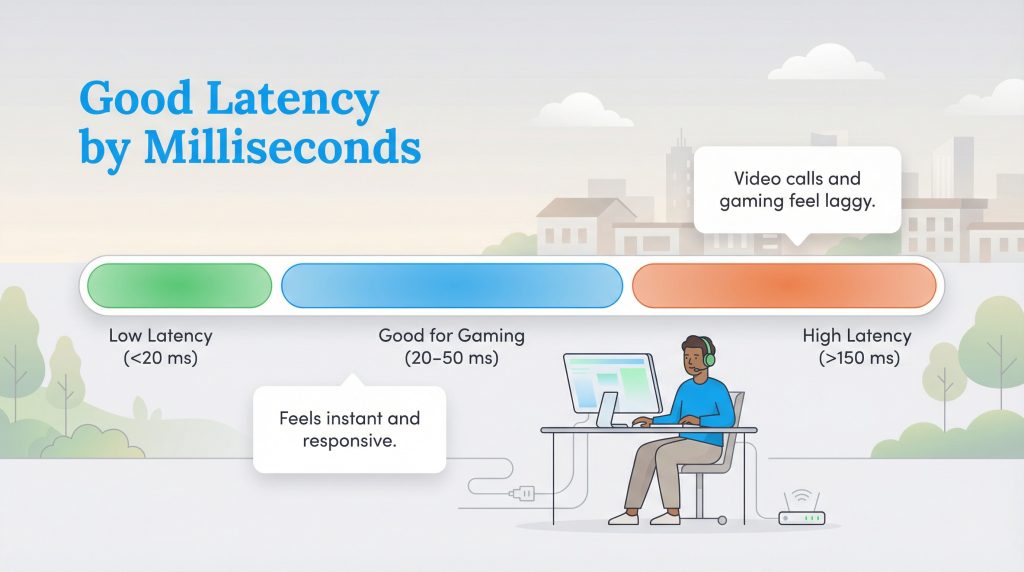
When you ask “what is a good latency,” the honest answer is: it depends on what you’re doing. For sending an email or browsing the news, you might not notice a slight delay. However, for real-time activities, every millisecond counts. Below is a breakdown to help you benchmark your current performance.
When looking at what is a good latency for gaming, you generally want to be under 50 ms, with anything under 20 ms being exceptional. Once you start creeping above 150 ms, you’re entering high-latency territory, where lag becomes noticeable and disruptive for almost any interactive task. That’s the basic high latency meaning: a slow reaction time that makes everything feel delayed.
| Activity | Good Latency (ms) | Acceptable Latency (ms) |
|---|---|---|
| Competitive Gaming | < 20 ms | 20–50 ms |
| Video Conferencing (Zoom) | < 50 ms | 50–100 ms |
| General Browsing/Email | < 100 ms | < 150 ms |
If your latency is consistently above the “acceptable” ranges for what you do most often, like gaming or daily video calls, it’s worth trying the fixes below or talking to your provider.
Common Causes of High Latency
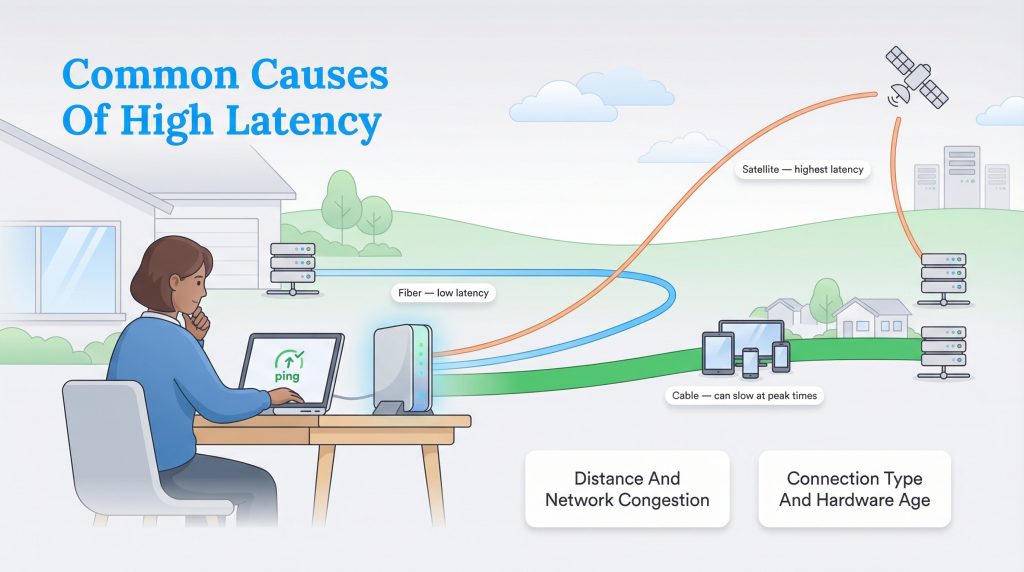
If your internet feels sluggish, several factors could be slowing down your data’s journey. Distance also plays a huge role. The physical distance between your home and the server you’re connecting to matters; connecting to a game server in another country will always result in higher ping than one in your state. Inside your home, network traffic can cause jams. If three people are streaming 4K video while you try to game, your router might struggle to process all that data quickly. Finally, outdated hardware can be a bottleneck. If your modem or router is several years old, it may not be able to process modern speeds efficiently, adding unnecessary delay to every request.
How Your Internet Connection Type Impacts Latency
The biggest factor is often your connection type. Fiber internet plans are the gold standard for low latency because fiber-optic networks carry data as light signals and are usually built with modern equipment and fewer bottlenecks. Cable internet is generally good but can suffer from congestion when everyone in your neighborhood is online. Satellite internet, on the other hand, naturally has high latency because the signal has to travel all the way to orbit and back, physics simply takes over.
How to Fix High Latency and Reduce Lag

If you’re tired of the lag, you don’t always need to switch providers immediately. The number one fix is often the simplest: use an Ethernet cable. Wi-Fi is convenient, but it’s prone to interference from walls, appliances, and neighbor’s signals. Hardwiring your computer or console directly to the router eliminates that interference and provides the most stable connection possible. If you’re gaming or working from home on a desktop or console, plugging in with Ethernet is one of the easiest ways to cut your ping.
You should also check what is running on your network. Close background apps like cloud backups (Dropbox, iCloud) or large game updates that might be hogging your connection. Sometimes, your router just needs a fresh start. Restarting your router, the classic “turn it off and on again”, clears its internal cache and can resolve temporary glitches. If you’re playing online games, choose servers closer to your region when possible, shorter distance usually means lower latency.
If you have tried all these steps and still experience high lag, it might be time to upgrade your plan. If you’re on DSL or satellite, investigate if fiber is available in your area, as the technology itself is superior for latency.
For more detailed information on broadband benchmarks and what you should expect from your service, you can visit the FCC’s Broadband Speed Guide.
Better Connectivity Starts With Understanding Latency
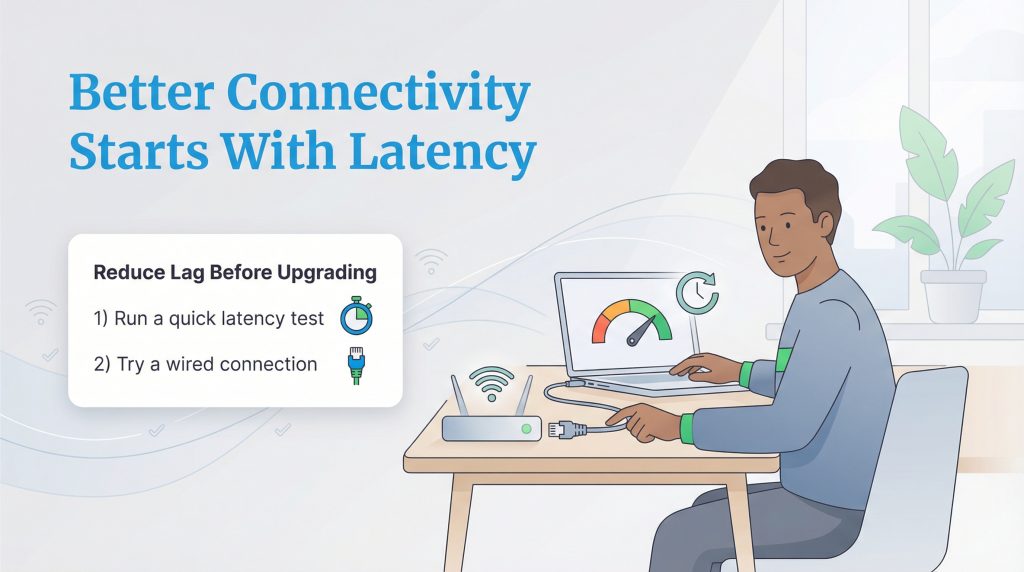
While internet speed is important, it isn’t the only metric that matters for a happy, connected home. Understanding latency gives you the power to troubleshoot why your video calls are choppy or why your smart home feels sluggish. Before you commit to a more expensive monthly bill, try running a simple test and switching to a wired connection. Often, a few small adjustments are all it takes to banish the lag and get back to a smooth, frustration-free experience.
FAQs About Internet Latency
What is the difference between latency and ping?
How do I check my internet latency?
Can a Wi-Fi extender fix latency?
Does higher bandwidth lower latency?
Why is my latency high at night?
About the Author
David has been an integral part of some of the biggest utility sites on the internet, including InMyArea.com, HighSpeedInternet.com, BroadbandNow.com, and U.S. News. He brings over 15 years of experience writing about, compiling and analyzing utility data.
