Understanding your power to choose can lead to lower rates and greener energy options
Key Takeaways
- Energy deregulation separates the supply of electricity from the delivery, allowing you to shop for competitive rates while your local utility still maintains the wires.
- You can lower your monthly bills or choose green energy by switching to a Retail Energy Provider (REP) instead of staying with the default utility rate.
- Your power reliability does not change when you switch providers; the local utility company is still responsible for fixing outages and maintaining infrastructure.
Energy deregulation might sound like a dry economic term, but it translates into a powerful advantage for you as a homeowner: the freedom to shop. Just as you compare prices for internet service, insurance, or groceries, deregulation allows you to compare electricity rates and pick the plan that fits your budget and lifestyle. Instead of being forced to buy power from a single monopoly, you can explore a marketplace full of options, can potentially save money, and access eco-friendly choices without sacrificing reliability.
What Is Energy Deregulation in Simple Terms?
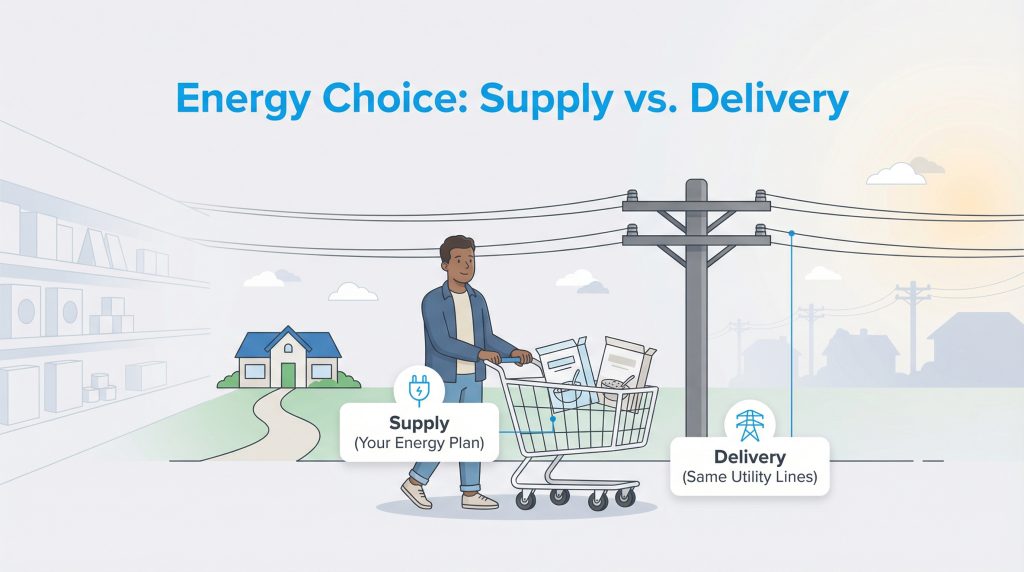
In the simplest terms, energy deregulation breaks the monopoly that traditional utility companies once held over the entire power system. Historically, one company generated the electricity, transported it, and sold it to you. In a deregulated market, these roles are split up. While the local utility company still owns and maintains the wires and poles, the actual electricity flowing through those wires is sold by competing companies. This system is often referred to as “Energy Choice.” If you’ve ever been told you can “shop for electricity” in your area, you’re living in an energy choice market.
Think of it like shopping for groceries. You can buy cereal from General Mills, Kellogg’s, or a generic brand, that is the “supply” or electricity. However, you use the same shopping cart and checkout lane to get your groceries to your car regardless of which brand you choose, that is the “delivery” or the utility lines. In a competitive market, retail energy providers compete for your business, which can drive down prices and spark innovation.
Regulated vs. Deregulated Markets: What’s the Difference?
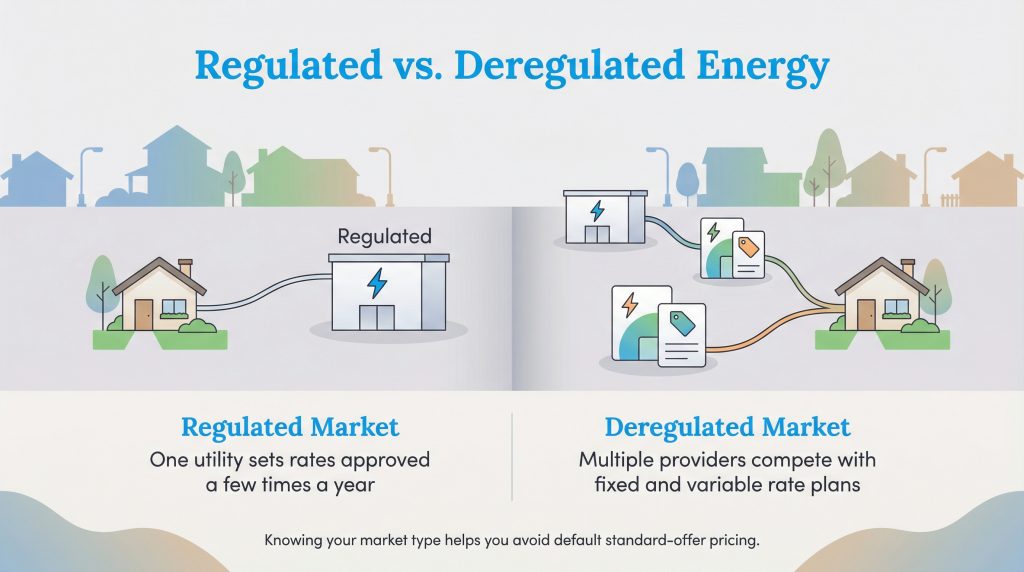
Understanding the difference between these two markets is key to taking control of your energy costs. In a fully regulated market, you have no choice; one utility company handles everything from generation to billing, and the state government sets the rates. In a deregulated market, you have the power to choose who generates your electricity, while the utility continues to deliver it. Here’s how regulated and deregulated systems compare from your point of view:
| Feature | Regulated Market | Deregulated Market |
|---|---|---|
| Who sells you power | Utility company only (Monopoly) | Competitive Retail Energy Providers (REPs) |
| Pricing | Set by state regulators and the utility | Driven by competition among suppliers |
| Billing | One bill for all services | One combined bill or separate bills (depending on provider) |
| Reliability | Utility is responsible | Utility is responsible |
The most important distinction here is pricing. In regulated states, rates are approved by a public commission and often change only once or twice a year. In deregulated areas, Retail Energy Providers offer various pricing structures, such as fixed rates that lock in your price for years or variable rates that fluctuate with the market. If you are setting up electric service in a new home, knowing your market type helps you avoid defaulting to a potentially higher “standard offer” rate.
How Deregulation Affects Your Bill: Utilities vs. Suppliers
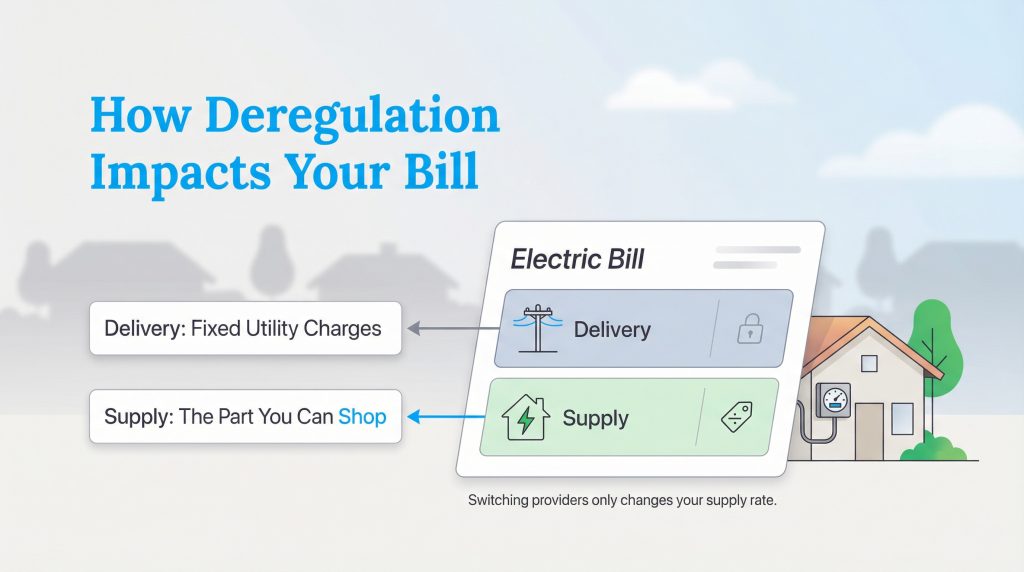
When you look at your electric bill in a deregulated market, you’ll notice the charges are split into two main categories. Understanding this “supply chain” split is crucial because you can only save money on one specific part of the bill. The first part is the Delivery or Transmission Charge. This money goes to your local utility company (often called a TDU or TDSP) to pay for maintaining the poles, wires, and meters. These rates are regulated and fixed; you cannot change them by switching companies.
The second part is the Supply or Generation Charge. This covers the cost of the actual electricity you use. This is the portion of the bill where energy choice comes into play. When you switch to a new Retail Energy Provider (REP), you are changing the company that supplies the power, and therefore, you are changing this specific rate. The delivery charges remain exactly the same, but securing a lower supply rate can significantly reduce your overall monthly total.
Look for a line on your bill labeled “Price to Compare” or “Supply Rate.” This is the rate your utility charges for supply, and you can use this number to see if a competitor is offering a better deal.
The Benefits of Energy Choice for Homeowners
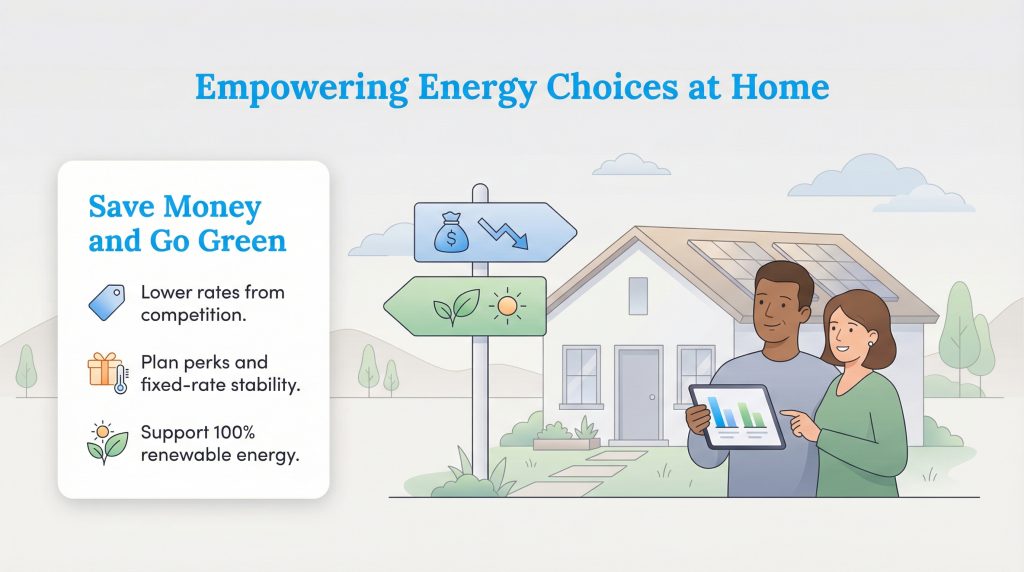
Why should you care about switching providers? The primary motivation for most homeowners is cost savings. Because providers are competing for your business, they often offer rates that are lower than the local utility’s default price, especially when market conditions are favorable. Competition also encourages perks; some companies offer incentives like gift cards, smart thermostats, or cash-back rewards to get you to sign up. Additionally, you can choose a plan structure that suits your financial goals, such as a fixed-rate plan that protects you from seasonal price spikes.
Beyond saving money, deregulation has become a major avenue for renewable energy adoption. In the past, you used whatever mix of coal, nuclear, or gas your utility provided. Now, you can specifically choose plans powered by 100% wind or solar energy. This allows renters and homeowners who cannot install rooftop panels to still support green energy and lower their carbon footprint instantly.
Eco Edge: Many deregulated providers offer “Green Plans” backed by Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs), which are credits tied to renewable generation. It is one of the easiest ways to reduce your home’s carbon footprint without installing hardware.
Is My State Deregulated?
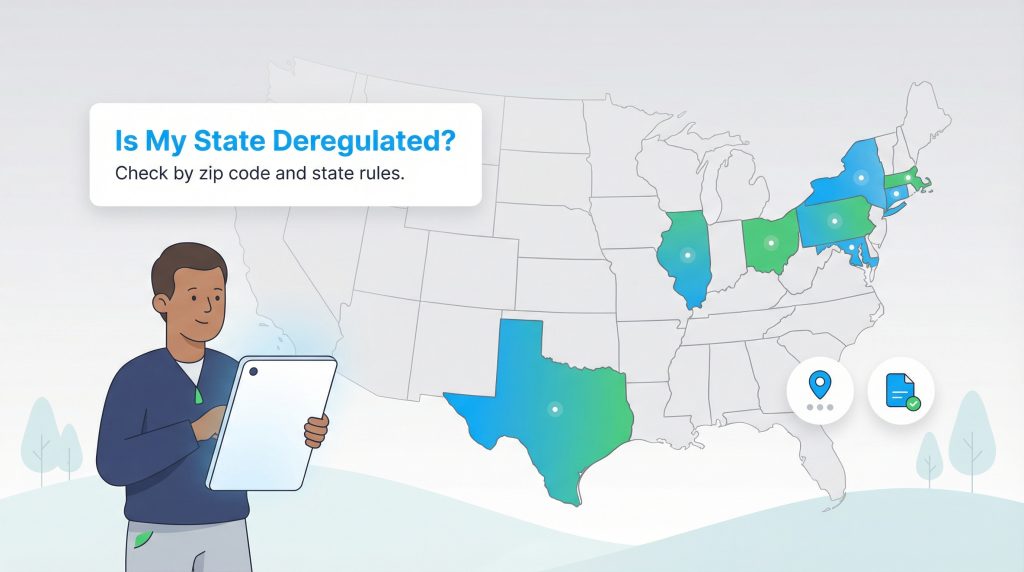
Energy deregulation is decided at the state level, meaning your ability to choose a supplier depends entirely on your zip code. Not every state has opened its market to competition, and some states have deregulated natural gas but not electricity, or vice versa. Currently, over a dozen states have active deregulated electricity markets for residential consumers.
Some of the major states where you can shop for electricity include Texas, Pennsylvania, Ohio, Illinois, New York, Maryland, Connecticut, and Massachusetts. It is worth noting that the rules vary by location; for example, Texas has a unique market where most residents in deregulated areas must choose a provider, whereas in Pennsylvania, shopping is optional. For authoritative information on energy markets, you can visit the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) or check your specific state’s public utility commission website.
Common Myths About Switching Providers

Despite the benefits, many people hesitate to switch because of persistent myths about safety and reliability. The most common fear is that “my power will go out if I switch.” In reality, your local utility company manages the grid regardless of who you buy power from. The electrons entering your home are identical, and your service will not be interrupted during a switch.
Another concern is financial security: “If the supplier goes bankrupt, I’ll be in the dark.” This is also false. Most deregulated markets have a default or “provider of last resort” service that automatically serves you if your supplier fails, often through the local utility or a designated backup provider. While you should always read the fine print to avoid scams, the market is monitored by state commissions. In states like Texas, you’ll see an “Electricity Facts Label” (EFL) or a similar standardized disclosure. Always review it so you understand the rate structure, fees, and contract length before signing up.
For more tips on how to manage your costs, check out our guide on how to save on your electric bill.
Take Charge of Your Energy Costs Today

Energy deregulation puts the power directly in your hands, transforming you from a passive ratepayer into an active consumer. By understanding how the market works, you can find a plan that offers price stability, lower rates, or cleaner energy without sacrificing the reliability you depend on. We encourage you to grab your most recent electric bill, identify your current rate, and spend a few minutes comparing offers in your area. A simple switch could keep more money in your pocket every month while also supporting cleaner, more eco-conscious energy sources.
FAQs About Energy Deregulation
Which states have energy deregulation?
Do I have to switch energy providers in a deregulated state?
Who do I call if my power goes out?
Can I really save money by switching suppliers?
What is a Retail Energy Provider (REP)?
About the Author
David has been an integral part of some of the biggest utility sites on the internet, including InMyArea.com, HighSpeedInternet.com, BroadbandNow.com, and U.S. News. He brings over 15 years of experience writing about, compiling and analyzing utility data.
