Key Takeaways
- Your TDU delivers electricity and maintains the grid. They’re separate from your power provider, handle outages, and you can’t choose them.
- TDU charges stay the same no matter your provider. Only the “supply” portion of your bill changes when you switch companies.
- Fees cover grid maintenance, reliability, and upgrades. They’re regulated to ensure fair pricing for essential infrastructure.
So, you’re shopping for a new electricity provider, but wait… what’s this “transmission and delivery utility” charge on your bill? And why does it matter when choosing an electricity plan?
What’s a Transmission & Delivery Utility?
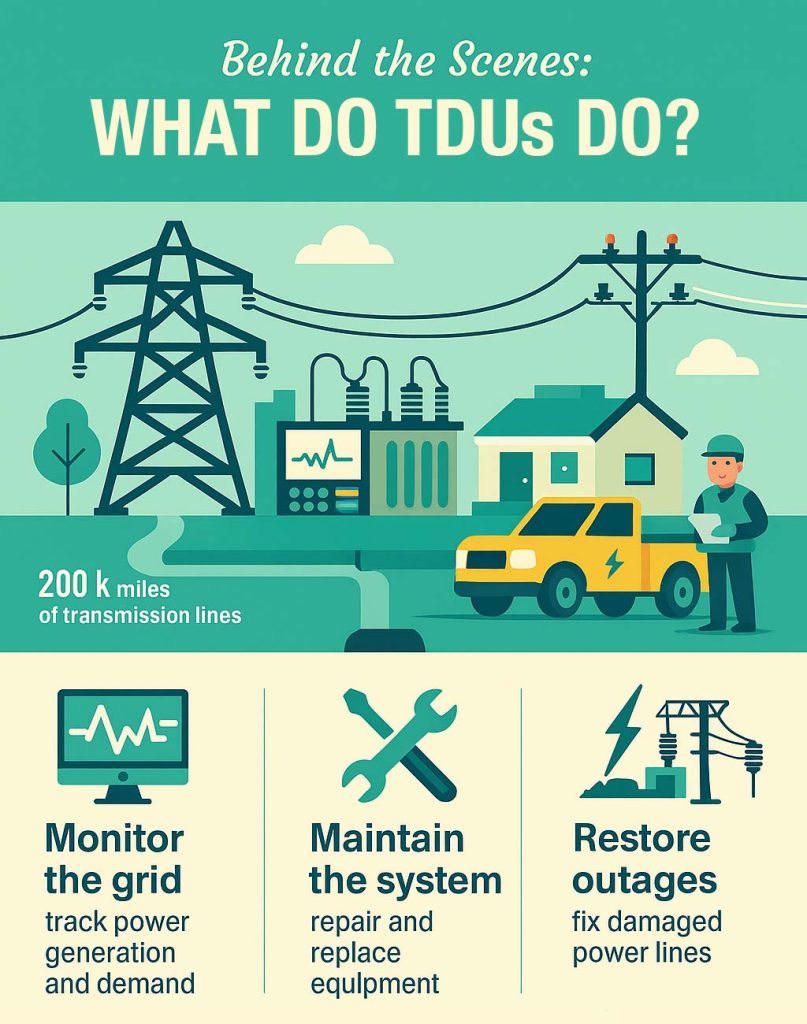
Think of your electricity like a package you order online. The retail electricity provider (the company you choose) is like the seller, they generate or buy the power. But the transmission & delivery utility (TDU) is like the shipping company that gets it to your door.
These utilities own and maintain the power lines, poles, transformers, and substations that bring electricity to your home. Even if you switch providers, this part stays the same, they’re the ones keeping the lights on (literally!).
Key Things a TDU does:
- Maintain the Grid: Fix outages, upgrade equipment, and keep everything running smoothly.
- Deliver Electricity: Transport power from generators (like wind farms or power plants) to your home.
- Handle Emergencies: Storm knocked out power? They’re the ones who send crews to fix it.
- Read Your Meter: They track how much electricity you use (so your provider can bill you correctly).
Understanding TDU Fees and What They Cover
Those “delivery charges” on your electricity bill can sometimes be confusing. Let’s break down exactly what you’re paying for when it comes to TDU fees.
What’s Included in Your TDU Charges?
Your monthly TDU fees typically cover these essential services:
1. Infrastructure Maintenance
- Power line repairs and upgrades
- Substation maintenance
- Pole replacements
- Transformer servicing
- Vegetation management (tree trimming near lines)
2. Operational Costs
- 24/7 emergency response teams
- Meter reading (even for smart meters)
- Customer service operations
- Billing systems
- Grid monitoring technology
3. System Improvements
- Grid modernization projects
- Storm hardening improvements
- Capacity expansions for growing areas
- Renewable energy interconnection upgrades
4. Regulatory Requirements
- Safety inspections
- Environmental compliance
- Cybersecurity protections
- Reliability standard investments
How TDU Fees Are Calculated
Most utilities use a combination of these rate components:
1. Base Charge: Flat monthly fee for being connected to the grid
2. Usage Charge: Cost per kWh that varies with your consumption
3. Demand Charge: For commercial customers (based on peak usage)
Example from Texas:
Oncor’s typical residential charges include:
- $4.25 monthly base charge
- 3.8¢ per kWh delivery charge
Why Fees Vary By Location
You might notice neighbors in different areas pay different TDU rates because of:
Urban vs. Rural
- Cities have more customers sharing costs
- Rural areas require more miles of lines per customer
Weather Risks
- Storm-prone areas invest more in resilient infrastructure
Growth Patterns
- Fast-growing regions need more capacity investments
Grid Age
- Older systems often require more maintenance
Reading Your Electric Bill
Look for these common TDU fee labels:
- “Delivery Charges”
- “Transmission Cost Recovery”
- “Distribution System Charge”
- “Pole and Wire Maintenance Fee”
Tips for Managing TDU Costs
While you can’t avoid TDU fees entirely, you can:
- Use energy efficiently to reduce variable charges
- Ask about budget billing options
- Check if your utility offers low-income assistance
- Participate in demand response programs if available
Remember: These fees ensure your lights stay on when you flip the switch, and your utility is required to justify all charges to regulators. If you see a significant unexplained increase, you can always contact your state’s public utility commission for clarification.
Major TDUs Around the Country
Now that you know what TDUs do, you might be wondering who these companies actually are. While there are hundreds of local utilities, here are some of the biggest players serving millions of customers nationwide:
Texas (ERCOT Market):
- Oncor: Serves Dallas/Fort Worth and much of North Texas
- CenterPoint: Covers the Houston metro area
- AEP Texas: Serves Corpus Christi, the Rio Grande Valley, and West Texas
Northeast/Mid-Atlantic:
- PSE&G (New Jersey)
- Con Edison (New York City)
- PECO (Philadelphia area)
Midwest:
West Coast:
- PG&E (Northern California)
- Southern California Edison (Los Angeles area)
Why Does This Matter When Choosing an Electricity Provider?
Now that you know what the utility does, you might wonder how this affects your choice of electricity provider. Here’s the important things to remember.
- You can’t pick your utility, it’s assigned based on where you live.
- Your electricity provider only sells you the power, the utility delivers it.
- Delivery charges stay the same no matter which provider you pick.
So when you compare plans, focus on the supply rate (the cost of the electricity itself) and the provider’s customer service, contract terms, and renewable energy options.
Will My Bill Change If I Switch Providers?
If you’re considering a new electricity provider, it’s natural to wonder how your bill will be affected. Your bill has two main parts:
- Supply Charges (from your new provider)
- Delivery Charges (from your local utility—this won’t change)
Switching providers only affects the supply portion. The utility’s fees are regulated and stay the same.
Now that you know how transmission and delivery utilities work, you can shop for electricity like a pro! Remember, your utility is like the highway your electricity travels on, it stays the same no matter whose “car” (electricity) is driving on it.
Understanding How TDUs Are Regulated
Now that you know what TDUs do and how they affect your electricity service, let’s talk about who keeps an eye on them to protect consumers like you.
Who Regulates Transmission & Delivery Utilities?
TDUs don’t operate in a free market, they’re carefully monitored by several government agencies to ensure fair pricing and reliable service. Here’s how it works:
State Public Utility Commissions (PUCs)
These are your frontline consumer protectors:
- Approve all rate changes and fee increases
- Set reliability standards (like outage response times)
- Investigate consumer complaints
- Review infrastructure investment plans
- Monitor service quality metrics
Each state has its own PUC with different names:
- Texas: Public Utility Commission of Texas (PUCT)
- California: California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC)
- New York: New York State Public Service Commission
Federal Oversight
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) regulates:
- Interstate transmission lines
- Wholesale electricity markets
- Large-scale grid reliability standards
Local Municipal Oversight
In some areas, city governments have additional authority over:
- Right-of-way permissions
- Local reliability requirements
- Aesthetic standards for equipment
Why Regulation Matters to You
These oversight systems exist to:
- Prevent monopolies from overcharging
- Ensure fair access to the grid for all providers
- Maintain consistent reliability standards
- Fund necessary grid improvements
- Protect vulnerable customers
How You Can Participate
Did you know you can voice opinions about TDU operations? Most PUCs allow:
- Public comment periods for rate cases
- Consumer complaint processes
- Public hearings about major projects
- Online portals to report service issues
Recent Regulatory Trends
Regulators are currently focused on:
- Modernizing aging infrastructure
- Supporting renewable energy integration
- Preparing for electric vehicle growth
- Improving outage communication systems
- Implementing smart grid technologies
Understanding this regulatory framework helps explain why certain decisions get made about your electricity service, and who to contact if you have concerns!
FAQs about TDUs
Can I choose my TDU?
Why do I pay separate TDU charges?
– Maintaining power lines and equipment
– Responding to outages
– Grid upgrades and improvements
– Meter reading services
Think of it like paying tolls to maintain the highways your electricity travels on.
Will my TDU charges change if I switch providers?
Who do I call during a power outage?
Why are TDU fees sometimes higher than the electricity cost?
Do TDUs offer different service quality?
– Faster outage response times
– More reliable equipment
– Better vegetation management (tree trimming)
– More frequent grid upgrades
You can compare reliability statistics for your TDU through your state’s utility commission.
Can I negotiate TDU fees?
How do renewable energy plans affect TDU charges?
Why do TDU charges vary by location?
– Population density
– Terrain challenges
– Age of infrastructure
– Local weather risks
Urban areas typically have lower per-customer delivery costs than rural areas.
Who regulates TDUs?
– Rate changes
– Service quality standards
– Approval of infrastructure projects
– Customer complaint resolution
Can I opt out of TDU services?
How often do TDU rates change?
About the Author
LaLeesha has a Masters degree in English and enjoys writing whenever she has the chance. She is passionate about gardening, reducing her carbon footprint, and protecting the environment.
