High jitter creates frustrating lag spikes, but simple hardware upgrades and network adjustments can smooth out your connection.
Key Takeaways
- Jitter is the variation in latency (ping) that causes stuttering in gaming and robotic audio in video calls.
- Ideally, your jitter speed should be below 30 milliseconds (ms) for a stable experience, especially for real-time activities.
- You can lower jitter by switching to a wired Ethernet connection, upgrading your router, or prioritizing traffic with QoS settings.
We’ve all been there: you’re about to make a crucial point on a video call or take the winning shot in a match of Call of Duty, and suddenly, everything freezes. You didn’t lose your internet connection entirely, but the stuttering, robotic audio, and “rubber-banding” made the experience impossible. While most people focus exclusively on high download speeds, the true hero of a smooth online experience is stability, measured by something called jitter. This guide explains exactly what jitter is, how it differs from your ping, and the practical steps you can take to fix it so you can get back to seamless gaming and streaming.
What Is Jitter in Networking?
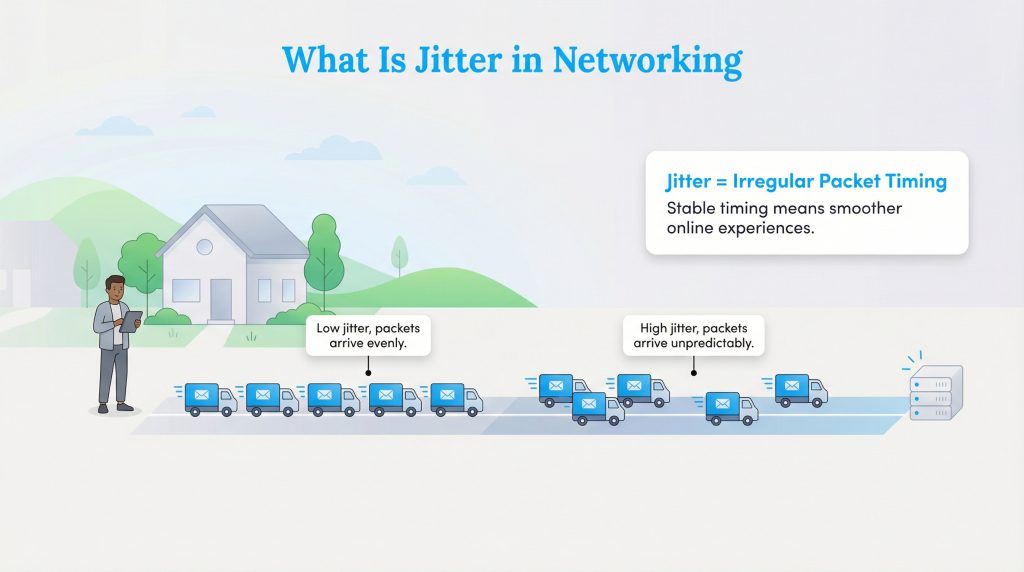
In simple terms, jitter is the inconsistency in the time it takes for data to travel from your device to the server and back. Technically known as Packet Delay Variation, it measures the stability of your connection. When you do anything online, data travels in small units called “packets.” If these packets arrive at irregular intervals, some fast, some slow, you experience jitter.
Think of your internet connection like a series of delivery trucks carrying mail to your house. In a low-jitter scenario, a truck arrives every single day at exactly 10:00 a.m. It is predictable and reliable. In a high-jitter scenario, one truck arrives at 9:00 a.m., the next one comes at 4:00 p.m., and the one after that doesn’t show up until noon the next day. Even if all the mail eventually arrives, the irregular timing creates chaos. In your network, this chaos manifests as glitches and lag.
Jitter vs. Ping vs. Latency: What’s the Difference?
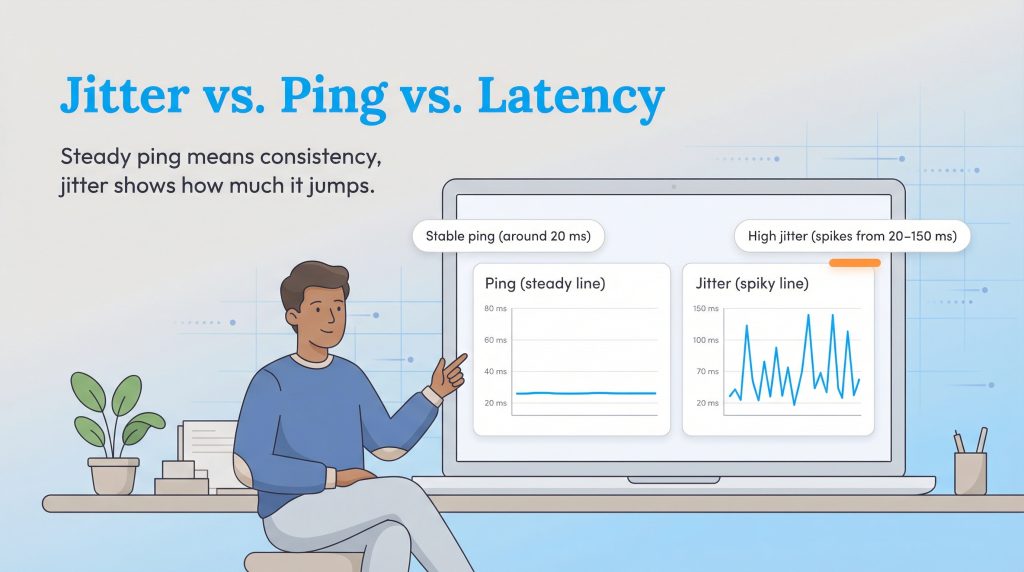
These terms are often used interchangeably, but understanding the difference between jitter vs. ping is key to diagnosing your connection health. You can have a fast internet speed (high bandwidth) and low ping but still suffer from high jitter, which makes your connection feel unstable.
| Metric | Definition | How it Feels |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | The total time it takes for a data packet to travel from point A to point B. | A general delay or “sluggishness” between your action and the result. |
| Ping | The tool used to measure latency, usually expressed in milliseconds (ms). | The number you see on your screen; high numbers mean slower reactions. |
| Jitter | The fluctuation or consistency of your ping over time. | Stuttering, glitchy audio, freezing, and characters teleporting in games. |
If your ping sits steadily at 20ms, your connection is excellent. If your ping jumps wildly from 20ms to 150ms and back down to 30ms, you have high jitter, which is often far more annoying than a consistently slow connection.
What Is a Good Jitter Speed?

Acceptable jitter levels depend entirely on what you are doing. If you are just browsing the web or sending emails, you might not notice high jitter at all. However, for real-time applications, industry standards (such as those from Cisco) generally recommend keeping jitter below 30ms. Here are some practical guidelines for home use:
- Great (0–30ms): This is the ideal range. It offers a smooth experience for competitive gaming, HD video conferencing, and VoIP calls.
- Acceptable (30–50ms): This is okay for most streaming and browsing. You might notice minor hiccups or brief drops in audio quality during calls.
- Poor (50ms+): At this level, you will experience noticeable lag. Voice calls may sound robotic, and you will likely experience “rubber-banding” in online games.
How Jitter Affects Online Gaming (And What’s Good Jitter for Gamers?)

For gamers, jitter is often the difference between winning and losing. While a low ping is important, a low jitter score is critical for consistency. In fast-paced games like Valorant, Fortnite, or Call of Duty, high jitter causes “rubber-banding”, where your character moves forward only to snap back to a previous position a second later.
So, what is a good jitter speed for gaming?
- Competitive Gaming: Aim for jitter under 10ms. This ensures your shots register instantly and movement feels fluid.
- Casual Gaming: Jitter under 30ms is generally acceptable and shouldn’t ruin your fun.
If you notice your character “teleporting” or hit registration feels off despite a decent ping, high jitter is likely the culprit. Prioritizing your gaming console or PC using Quality of Service (QoS) settings or switching to a wired connection are the best ways to solve this.
Common Causes of High Jitter

Understanding why jitter happens is the first step toward fixing it. Several factors inside and outside your home can cause these data packets to get delayed.
Network Congestion
Just like a highway during rush hour, your home network can get jammed. If someone is streaming 4K video in the living room while you try to game in the bedroom, your router may struggle to process all the data packets simultaneously, causing delays.
Wireless Interference
Wi-Fi is convenient, but it is inherently unstable compared to wired connections. Signals have to travel through walls and furniture, and they can be disrupted by other electronic devices like baby monitors or microwaves. This interference causes packets to get lost or delayed.
Old Hardware
If your router or modem is several years old, it may not be able to handle modern speeds or multiple devices efficiently. Older routers using the DOCSIS 3.0 standard often don’t handle heavy traffic as efficiently as newer DOCSIS 3.1 models, which can contribute to latency and jitter issues.
Connection Type
The type of internet you have plays a massive role. Fiber internet typically offers the lowest jitter because light signals travel incredibly fast and aren’t subject to electromagnetic interference. Satellite and 5G connections often have higher jitter because the signal has to travel through the air over long distances or varies with signal strength.
| Connection Type | Typical Jitter | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Optic | Very Low (0–10ms) | Competitive gaming, work-from-home, heavy streaming. |
| Cable (Coax) | Low to Moderate (10–40ms) | General use, casual gaming, family households. |
| 5G Home Internet | Variable (20–100ms+) | Flexibility, renters, areas without wired options. |
| Satellite | High (50ms+) | Rural areas with no other reliable access. |
Eco Edge: Fiber optics are not only faster but also more energy-efficient than older copper cable infrastructure. Switching to fiber can reduce the overall energy consumption of your internet service.
How to Test and Measure Your Jitter

You can easily find your jitter score using free online tools. Most standard internet speed or “jitter internet test” tools will display jitter alongside your download and upload speeds.
We recommend using a reputable service like Speedtest.net. When you run the test, look for the “Jitter” metric in the detailed results view. For the most accurate diagnosis, run the test twice: once while connected via Wi-Fi and once while plugged directly into your router with an Ethernet cable. This will help you determine if the problem is your internet service provider (ISP) or just your Wi-Fi signal.
How to Fix Jitter and Reduce Lag

If your test results show high jitter, don’t panic. There are several actionable steps you can take to stabilize your connection, ranging from free settings adjustments to hardware upgrades.
Use a Wired Ethernet Connection
This is the single most effective way to fix jitter. Wi-Fi is prone to interference, but a wired connection is a direct pipeline for data. Connecting your computer or gaming console directly to your router using a CAT6 Ethernet cable often eliminates jitter instantly. It’s a simple, low-tech solution that provides the best stability.
Prioritize Traffic with Quality of Service (QoS)
Most modern routers have a feature called Quality of Service (QoS). This allows you to tell your router which devices or applications are most important. You can set your router to prioritize traffic to your work laptop or Xbox over the kids’ iPad streaming YouTube. This ensures your critical data packets get sent first, preventing lag spikes even when the network is busy.
Update and Reboot Your Equipment
Sometimes the simplest fix is the best one. Routers and modems are tiny computers that can get “clogged” with temporary data errors over time. Rebooting your modem and router can clear these errors and refresh your connection channel. Additionally, check your router’s manufacturer app to ensure you have the latest firmware updates installed for optimal performance.
Reduce Competing Traffic
Heavy bandwidth usage in the background is a silent jitter killer. Schedule large file downloads, cloud backups, or game updates for the middle of the night when no one is using the internet. If you are about to set up your home internet for a gaming session or an important meeting, ask others in the house to pause 4K streaming temporarily.
Upgrade Your Router or Modem
If your router is more than five years old, it might be the bottleneck. Newer routers supporting Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) are designed to handle many devices at once without dropping packets. Investing in durable, high-quality hardware is also a smart sustainability move, as better equipment lasts longer and reduces electronic waste over time.
Switch to a Fiber Internet Provider
Sometimes the issue isn’t your equipment, it’s the connection itself. If you are on DSL, fixed wireless, or satellite internet, high jitter might be unavoidable due to the technology’s limitations. If available in your area, switching to a fiber internet provider is the “Gold Standard” for low latency and jitter.
Improving Your Home Network for the Long Term
While you cannot control the internet traffic outside your home, you have full control over the setup inside it. Taking the time to optimize your network with quality cables, modern hardware, and proper configuration saves you from the headache of dropped calls and lost games. Investing in a stable setup now not only improves performance but also ensures your digital life runs smoothly for years to come, avoiding the waste and cost of constantly replacing cheap, inefficient equipment. For more tips on balancing performance and cost, check out our guide on how to save on your internet bill.
FAQs About Jitter
Is 0 jitter possible?
Does a fast download speed mean low jitter?
Why is my jitter high on Wi-Fi but fine on Ethernet?
Can a VPN fix jitter?
How do I lower jitter on PS5 or Xbox?
About the Author
LaLeesha has a Masters degree in English and enjoys writing whenever she has the chance. She is passionate about gardening, reducing her carbon footprint, and protecting the environment.
