Understanding why data packets go missing is the first step toward smoother streaming, gaming, and video calls.
Key Takeaways
- Packet loss happens when data traveling across a network fails to reach its destination, causing lag, buffering, or frozen video calls.
- Common causes range from network congestion and outdated hardware to faulty cables or issues with your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
- You can often fix packet loss yourself by switching to a wired Ethernet connection, updating software drivers, or prioritizing traffic via Quality of Service (QoS) settings.
There are few things more frustrating than being in the middle of a crucial work presentation or a competitive online game only to have your screen freeze or your audio cut out. While many people immediately blame their internet speed, the real culprit is often packet loss. This is especially common when you’ve just moved into a new home or rearranged your home office, potentially disrupting the signal path. Although the term sounds technical, it refers to a very common issue where small units of data fail to arrive at their destination, leaving gaps in your connection. Fortunately, diagnosing this problem is straightforward, and you can usually resolve it with a few simple adjustments to your home network setup.
What Is Packet Loss? (The Simple Explanation)
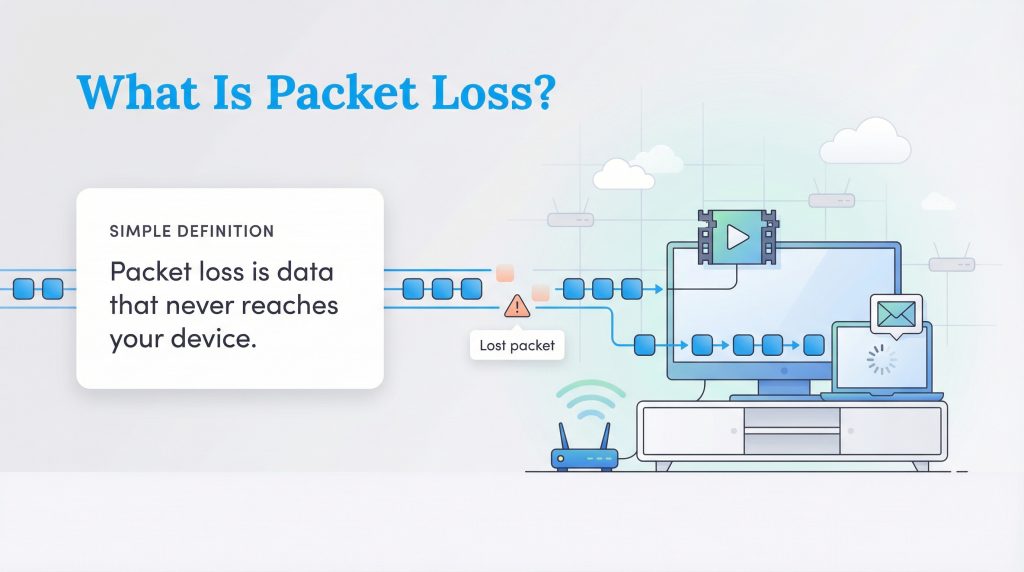
In simple terms, packet loss is when units of data fail to reach their destination. To understand packet loss, you first need to understand how the internet works. Everything you do online, sending an email, watching a movie, or playing a game, is broken down into tiny units called “packets.” These packets travel from a sender (like a Netflix server) through a vast network of cables and routers to reach a receiver (your laptop or TV). Once they arrive, your device reassembles them into the image or sound you see.
Think of this process like mailing a letter. You write a message, put it in an envelope, and drop it in the mailbox. Ideally, the postal service delivers it safely to your friend. But if that letter falls out of the truck or gets stuck in a sorting machine, your friend never receives the message, or they only get part of it. In the digital world, when these data packets get “lost in the mail” and fail to reach your device, it results in packet loss. This forces your computer to wait for the data to be resent, creating the delays and glitches you experience as lag.
Signs You Are Experiencing Packet Loss

If you are wondering “Do I have packet loss?” these are the signs to watch for. Because different online activities handle data differently, packet loss doesn’t always look the same. If you are just reading a news article, you might not notice a missing packet at all because the page simply takes a fraction of a second longer to load. However, real-time activities are much more sensitive to these dropped data units. Here is how packet loss typically manifests across different tasks:
- Work-From-Home (WFH): You might experience choppy audio on Zoom or Microsoft Teams, hear robotic-sounding voices, or see video feeds freeze while the audio continues.
- Gaming: Players often experience “rubberbanding,” where characters seem to jump around the screen randomly, or suffer from sudden lag spikes and high ping.
- Streaming and Browsing: You will likely encounter endless buffering wheels, pixelated video quality, or webpages that load slowly or incompletely.
- Smart Home Devices: Security cameras may stutter or fail to record continuously, and smart speakers might be slow to respond to voice commands.
Acceptable Packet Loss Rates: How Much Is Too Much?

In a perfect world, your packet loss rate would be 0%, meaning every piece of data sent arrives safely. However, the internet is a complex web of infrastructure, and minor hiccups happen. The amount of packet loss you can tolerate depends entirely on what you are doing. While a small percentage might be unnoticeable while browsing the web, that same amount can ruin a competitive gaming session or a job interview.
| Activity | Acceptable Rate |
|---|---|
| Browsing/Email | Up to 1-2% (Often tolerable, though 0% is ideal) |
| Streaming (Netflix/YouTube) | Less than 1% (Ideally 0%; buffering can mask small losses) |
| Online Gaming | As close to 0% as possible (Even 1-2% can cause issues) |
| VoIP/Video Calls | Less than 1% recommended (Quality degrades above this) |
Common Causes of Packet Loss in the Home

Understanding why packets get lost is the key to fixing the problem. While issues can sometimes occur on your Internet Service Provider’s end, the bottleneck is frequently inside your own home. Several factors can disrupt the flow of data, ranging from physical hardware damage to invisible signal interference.
1. Network Congestion
Just like a highway during rush hour, your home network has a limit on how much traffic it can handle. If you are on a video call while someone else is streaming a 4K movie and another person is downloading a large file, your bandwidth gets maxed out. When this happens, your router may drop packets simply because it cannot process them fast enough.
2. Wireless Interference
Wi-Fi is convenient, but it is also vulnerable. Signals can struggle to penetrate thick walls, metal appliances, or large furniture. Additionally, if you live in an apartment complex, your neighbors’ Wi-Fi networks may be competing for the same frequency, causing radio interference that disrupts your data transmission.
3. Outdated Hardware
Technology moves fast, and an old router or modem may struggle to keep up with modern internet speeds and heavy data loads. Older hardware often lacks the processing power to manage multiple devices efficiently. Upgrading to ENERGY STAR certified networking equipment can help you handle higher speeds while reducing “phantom load” energy consumption. Reducing energy waste also helps lower your electric bill.
4. Faulty Cables
Physical connections matter. If the Ethernet cables connecting your modem to your router are frayed, bent, or chewed by pets, they cannot transmit data reliably. This physical damage is a frequent, yet often overlooked, cause of data corruption.
5. Router Configuration Issues
Sometimes the issue isn’t physical but digital. Outdated firmware or misconfigured settings on your router can lead to inefficient data handling, causing packets to drop before they even leave your home network.
How to Test for Packet Loss

Many people assume a standard speed test will identify connection problems, but speed tests mainly measure bandwidth, how much data you can move at once. They do not always catch stability issues like packet loss. To get an accurate diagnosis, you need to run a packet loss test specifically designed to track dropped data packets over time.
You can use free browser-based tools like PacketLoss.com (not affiliated with us) to get a visual representation of your connection’s health. For Windows users comfortable with a bit more tech, you can use the Command Prompt. Simply type ping google.com -n 25 and hit Enter. This command sends 25 packets to Google and tells you how many of those test packets failed to return. If the result shows anything other than “0% loss,” you have a stability issue to address.
How to Fix Packet Loss: 5 Actionable Steps

Once you have confirmed you are losing packets, you can take specific steps to stabilize your connection. Most of these fixes are free and take only a few minutes to try.
1. Restart Your Router (Power Cycle)
It is the classic tech support advice for a reason. Routers are small computers, and over time their memory can get clogged with temporary data or minor software bugs. Unplugging your router for 30 seconds and plugging it back in clears this short-term memory and forces the device to re-establish a fresh connection with your ISP.
2. Switch to a Wired Connection (Ethernet)
Wi-Fi is inherently less stable than a physical cable because the signal travels through the air and encounters obstacles. If you need a rock-solid connection for gaming or important meetings, use an Ethernet cable to connect your computer directly to the router. This eliminates wireless interference entirely. For more on optimizing your home setup, check out our internet guides.
3. Check for Software/Driver Updates
Sometimes the hardware is fine, but the software telling it what to do is outdated. If you are using a PC, check your Device Manager to ensure your network adapter drivers are up to date. You should also log into your router’s admin panel to see if there is a firmware update available. Old drivers and firmware can cause compatibility issues that lead to dropped packets.
4. Enable QoS (Quality of Service)
Most modern routers have a feature called Quality of Service (QoS). This setting allows you to prioritize specific types of traffic. You can tell your router that your Zoom calls or gaming data are more important than a file download running in the background. For example, you can prioritize your work laptop or gaming console in the settings to ensure they get first dibs on bandwidth. This prevents non-urgent tasks from hogging all the bandwidth.
5. Replace Old or Damaged Cables
If you are using an old Ethernet cable you found in a drawer, it might be time for an upgrade. Cables are rated by category (like Cat5e, Cat6, or Cat8). Using a modern Cat6 cable ensures your physical connection can handle high speeds without errors. This is a cheap fix that often solves persistent stability problems.
When to Call Your ISP

If you have tried restarting your equipment, switching to Ethernet, and checking your cables but are still seeing packet loss, the issue likely lies outside your home. The “last mile” of infrastructure, the cables running from the street to your house, can degrade over time due to weather or age.
In this case, you should contact your Internet Service Provider. They can run diagnostic tests from their end to see if the signal dropping occurs before it even reaches your modem. If there is damage to the external lines, they will need to send a technician to repair it. Before you call, it helps to document your test results (like taking a screenshot of your packet loss test) to show the support agent exactly what is happening.
Enjoying a Smoother, Faster Connection

Packet loss is an annoyance that can disrupt your digital life, but it is rarely a permanent problem. By understanding the basics of how your network operates and testing for stability rather than just speed, you can pinpoint the issue quickly. Whether it’s a simple router restart or replacing a worn-out cable, taking these small steps will ensure you get the seamless, high-quality internet experience you pay for. By keeping your network efficient and stable, you’ll save time, frustration, and even a bit of energy at home.
FAQs About Packet Loss
Is 1% packet loss bad?
What is the difference between packet loss and latency?
Can a bad Ethernet cable cause packet loss?
Does a faster internet plan fix packet loss?
Why do I only get packet loss at night?
How do I run a packet loss test?
About the Author
LaLeesha has a Masters degree in English and enjoys writing whenever she has the chance. She is passionate about gardening, reducing her carbon footprint, and protecting the environment.
