Low latency is the secret to smooth gaming, clear video calls, and a responsive smart home.
Key Takeaways
- Ping measures the reaction time of your internet connection, representing how fast data travels from your device to a server and back.
- A ping under 50 ms is generally considered good for most online activities, while competitive gaming often requires speeds under 20 ms.
- Using a wired Ethernet connection is the most effective way to instantly lower your ping and stabilize your internet performance.
There are few things more frustrating than the dreaded “lag”, that moment when your video game character freezes in place right before a critical move, or your voice stutters and drops during an important Zoom presentation. We often blame our internet speed for these hiccups, rushing to upgrade to faster plans with higher download numbers. However, pure speed isn’t always the issue. The real culprit is often “ping.” While bandwidth determines how much data you can move, ping determines how responsive that data is. In this guide, we will demystify the tech jargon, explain exactly what is ping, and help you get the snappy, seamless connection you deserve.
What Is Ping and How Does It Work?
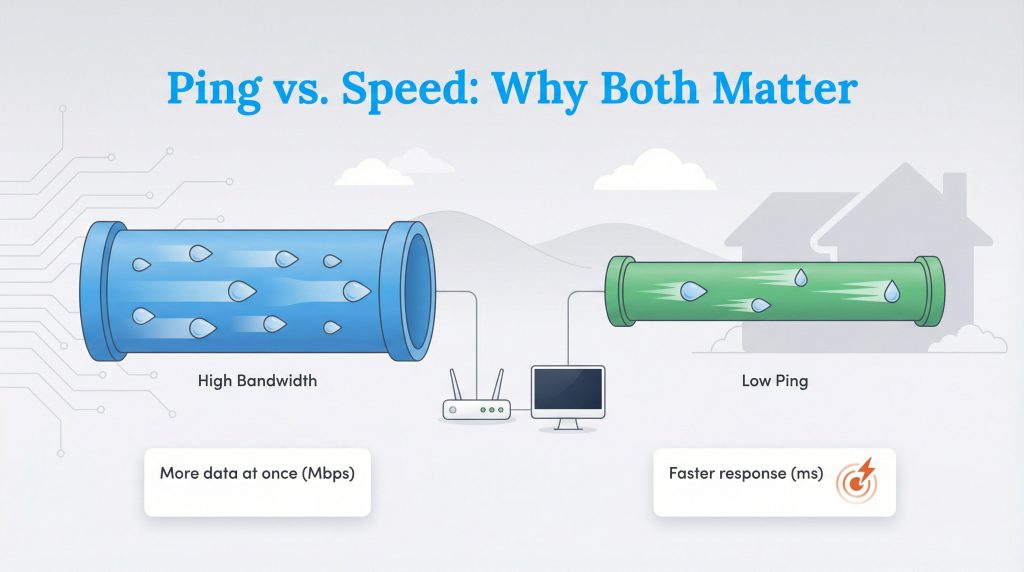
At its core, ping is a measurement of the reaction time of your connection. It represents the time it takes for a signal to leave your computer, travel to a server (like a website or game host), and return with a response. This round-trip time is measured in milliseconds (ms).
To understand the difference between speed and responsiveness, think of the Water Pipe Analogy. Bandwidth (download speed) is the width of the pipe. A wider pipe allows a massive amount of water to pass through at once, which is great for downloading large files. However, ping (latency) is how fast the water travels through that pipe. You can have a massive pipe, but if the water trickles through slowly, you still have a delay. High bandwidth helps you stream 4K movies, but low ping makes your clicks feel instant.
When you are shopping for internet plans, you will usually see providers advertising massive download speeds. Just remember that for activities requiring real-time interaction, keeping your milliseconds low is just as important as keeping your megabits high.
What Is a Good Ping Speed?

Because ping measures delay, a lower number is always better. However, “good” is relative to what you are trying to do. If you are just reading the news, a slight delay is unnoticeable. If you are trying to shoot a moving target in a competitive video game, even a fraction of a second matters.
| Ping Range (ms) | Status | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| 0–20 ms | Excellent | Competitive gaming, live streaming |
| 20–50 ms | Good | Casual gaming, video calls (Zoom/Teams) |
| 50–100 ms | Average | Web browsing, HD streaming |
| 100+ ms | Poor | Noticeable lag, rubber-banding, audio delays |
Understanding these ping ranges helps you set realistic expectations. Many home fiber and cable connections can often fall in the 20–50 ms range, which is perfectly adequate for the average household. If you consistently see numbers climbing above 100 ms, you are likely experiencing issues that need troubleshooting.
Why Ping Matters: Gaming, Work, and Smart Homes
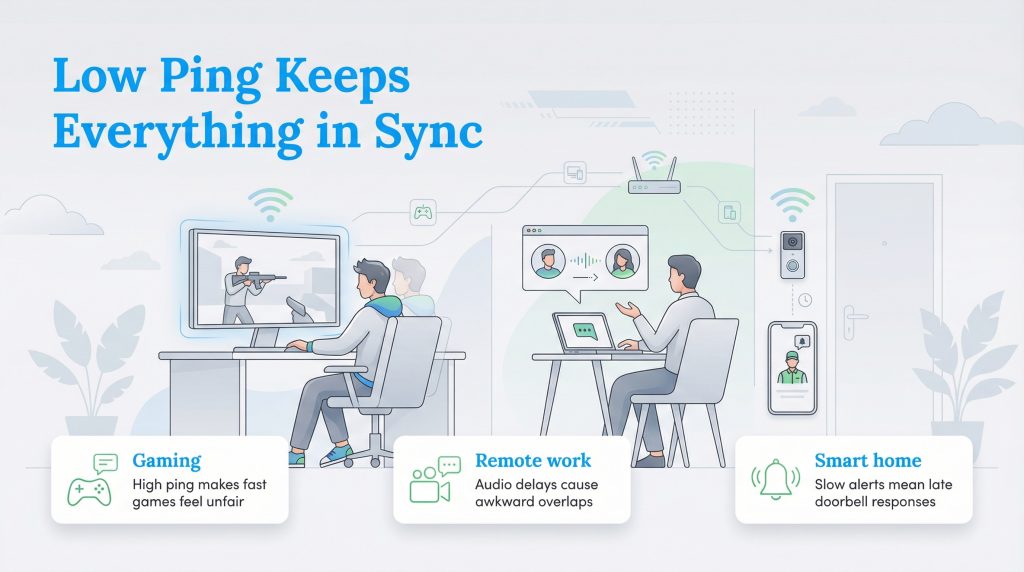
While gamers are usually the ones obsessing over what is a good ping speed, latency affects almost every interactive device in your home. Here is how high ping impacts different areas of your digital life:
What Is Ping in Gaming and Why It Feels Like a Handicap
If you have ever wondered “what is ping in gaming,” it is essentially your handicap. High ping causes “rubber-banding,” a visual glitch where your character (or an opponent) snaps back to a previous location because the server and your computer disagree on where everyone is. In fast-paced First-Person Shooter (FPS) games, a ping over 50 ms can mean you lose a match before you even see the opponent move.
For Remote Work
Remote work lag is a major productivity killer. High latency is responsible for those awkward moments on Zoom or Teams where two people accidentally talk over one another. Even if your video picture is crisp (thanks to good bandwidth), high ping creates a delay in the audio. You think the other person has finished speaking, so you start talking, only to realize they were still mid-sentence.
For Smart Homes
Your smart home relies on snappy communication between devices. Smart home latency can cause a frustrating delay between a motion sensor triggering and your phone receiving the notification. If you have a smart video doorbell, high ping might mean the delivery driver is already walking back to their truck by the time you can say “hello” through the app.
Ping vs. Jitter vs. Packet Loss
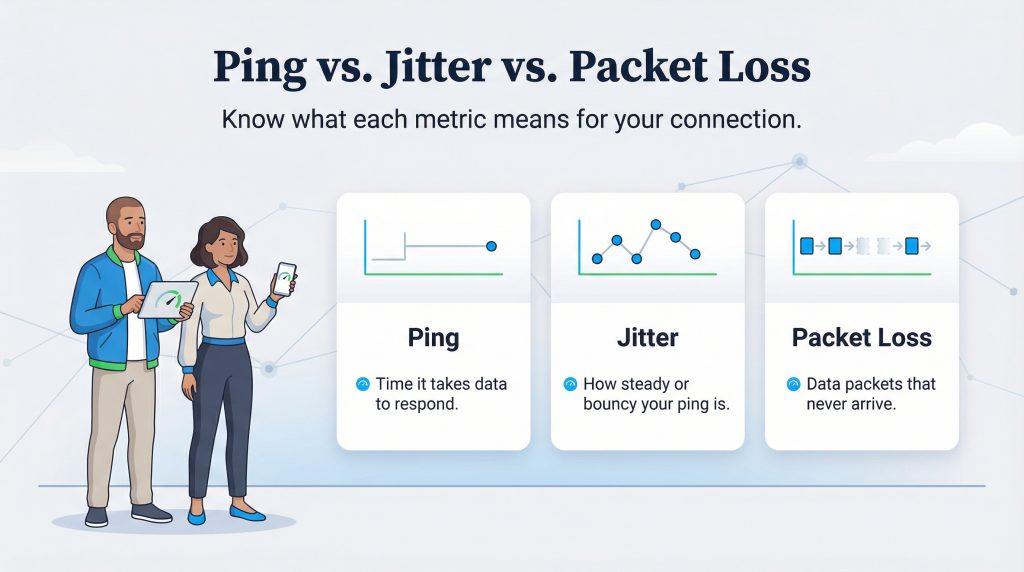
When you run an internet speed test, you might see terms other than just download speed and ping. Understanding these can help you diagnose exactly why your connection feels “off.”
Jitter measures the consistency of your ping. If your speed test shows high ping jitter, it means your connection’s delay is bouncing around instead of staying steady. Imagine you are having a conversation with someone who speaks at a steady rhythm, that is low jitter. Now imagine they speak three words fast, pause for five seconds, then shout the next ten words. That is high jitter. If your ping jumps from 20 ms to 100 ms constantly, your connection will feel stuttery and unreliable, even if the average speed looks okay.
Packet Loss is even more disruptive. Data travels across the internet in small units called “packets.” Packet loss occurs when some of these units get lost in transit and never reach their destination. This results in robotic, choppy audio during calls or characters disappearing entirely in games. For more details on broadband performance metrics, the FCC provides excellent consumer guides on what to expect from different services.
5 Ways to Lower Your Ping and Reduce Lag
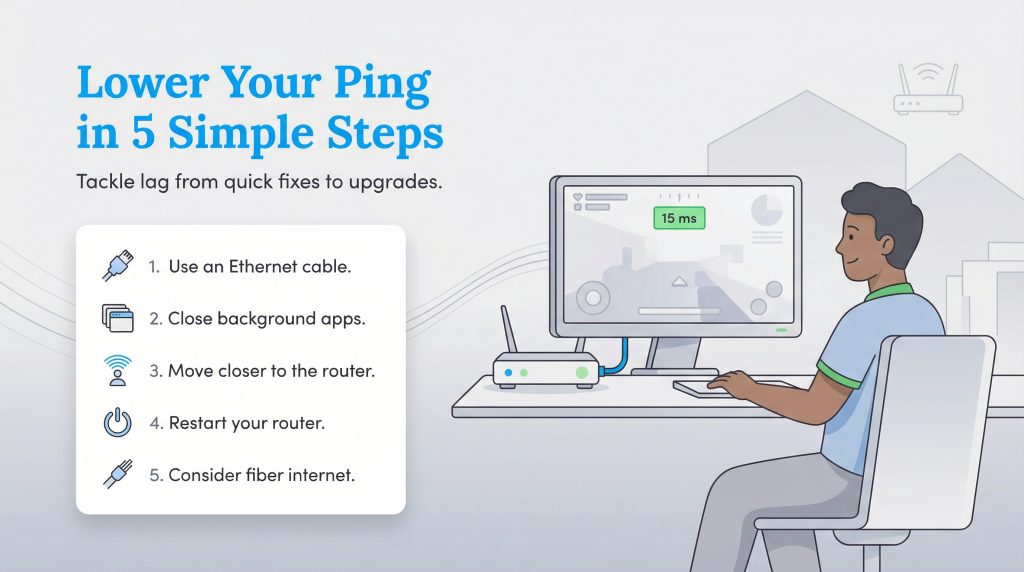
If your speed test results show high latency, don’t panic. You can often fix high ping without changing your internet provider. Here are five actionable steps to lower your ping, ordered from the simplest fixes to hardware upgrades.
- Use an Ethernet Cable: This is the single most effective way to lower ping for gaming and video calls. Wi-Fi signals are subject to interference from walls, microwaves, and neighbor’s networks. A physical Ethernet cable provides a direct, interference-free highway for your data.
- Close Background Apps: You might not realize that a cloud backup service, a large game update, or a 4K stream running in the other room is clogging your connection. These activities consume bandwidth and create data queues, which increases the time it takes for your important data to get through.
- Move Closer to the Router: If you absolutely must use Wi-Fi, distance is your enemy. Every wall and floor your signal has to penetrate adds milliseconds to your ping. Moving your setup into the same room as the router can make a surprising difference.
- Restart Your Router: It is a cliché for a reason. Routers have internal memory and caches that can get bogged down over time. A simple restart clears the cobwebs and forces the device to re-establish fresh routes to your ISP, often clearing up temporary lag spikes.
- Consider Fiber Internet: If you have tried everything and your ping is still high, the type of internet connection you have might be the bottleneck. Fiber optic internet naturally offers much lower latency than cable, DSL, or satellite because it uses light signals that travel faster and are less susceptible to interference.
The Key to a Snappier Connection at Home
While download speeds get all the attention in marketing commercials, ping is what determines the “feel” of your internet experience. It is the difference between a seamless video call and a frustrating, choppy conversation. By understanding what ping is and implementing simple tweaks, like prioritizing a wired connection or managing background downloads, you can transform a sluggish network into a responsive one. Now that you know what the numbers mean, we encourage you to run a speed test and see if your connection is as snappy as it should be.
FAQs About Ping
How do I check my ping?
Why is my ping so high but my internet is fast?
Does a better router improve ping?
Is 0 ms ping possible?
Does a VPN increase ping?
About the Author
LaLeesha has a Masters degree in English and enjoys writing whenever she has the chance. She is passionate about gardening, reducing her carbon footprint, and protecting the environment.
