Understanding how this government agency influences your energy bills, protects your consumer rights, and ensures safe service delivery.
Key Takeaways
- A Public Utilities Commission (PUC) is a state agency responsible for regulating essential services like electricity, natural gas, water, and telecommunications.
- These commissions often go by different names depending on your state, such as Public Service Commission (PSC) or Utility Regulatory Commission (URC).
- Beyond setting rates, the PUC allows consumers to file formal complaints against utility providers if issues cannot be resolved directly with the company.
Moving into a new home often comes with a flurry of paperwork, setup fees, and confusing acronyms, but few organizations impact your monthly budget and daily comfort as much as the Public Utilities Commission. Whether you’re wondering why your electric rate just went up, trying to dispute an unfair bill, or curious about solar incentives in your area, this agency is the invisible hand guiding the services you rely on. In this guide, we’ll break down exactly what a PUC is, how it differs from federal regulators, and the specific steps you can take to make your voice heard if your service falls short.
What Is a Public Utilities Commission (PUC)?

A Public Utilities Commission is a state-level government agency tasked with regulating the rates and services of essential public utilities. This includes the electricity that powers your lights, the natural gas heating your home, the water coming from your tap, and often your landline telecommunications services. While the specific PUC meaning in utilities context is about regulation, the agency’s primary mission is to balance the needs of consumers with the financial health of utility providers. They ensure that you receive safe, reliable, and reasonably priced service while allowing utility companies to earn a fair return on their infrastructure investments.
It’s important to note that the name of this agency varies significantly depending on where you live. You might be searching for the difference between a Public Service Commission vs Public Utility Commission, but in practice, they are usually the same type of entity with a different label. For example, California and Texas have a Public Utility Commission (PUC), while New York and Florida operate under a Public Service Commission (PSC).
What Does a Public Utilities Commission Do?

If you’re asking, “What does a Public Utility Commission do?” on a day-to-day basis, the answer involves a mix of financial oversight, safety inspections, and legal arbitration. These agencies serve as the “referee” between utility monopolies and the customers they serve. Their responsibilities generally fall into three core pillars that directly affect your home life.
Rate Setting
Utility companies cannot simply raise their prices whenever they want. Instead, they must file a “rate case” with the commission to request an increase. The PUC reviews these requests in public hearings to determine if the hike is justified by actual costs, such as infrastructure upgrades or rising fuel prices. If the commission deems the request excessive, they can deny it or approve a smaller increase to keep your bills manageable.
Safety and Reliability
Ensuring the lights stay on and the water stays clean is a massive operational challenge. The commission sets strict standards for infrastructure maintenance and safety. This involves inspecting pipelines, monitoring grid stability for electricity, and mandating upgrades to aging systems to prevent accidents or widespread outages.
Consumer Protection
Perhaps the most direct benefit to you is the commission’s role in dispute resolution. If you have a billing error that your provider refuses to fix, or if you’re facing an unfair service shutoff, the PUC provides a formal avenue for recourse. They enforce rules that prevent predatory practices, ensuring that customers of natural gas, electric, and water utilities are treated fairly.
Regulated vs. Deregulated States: How the PUC Affects Your Choice
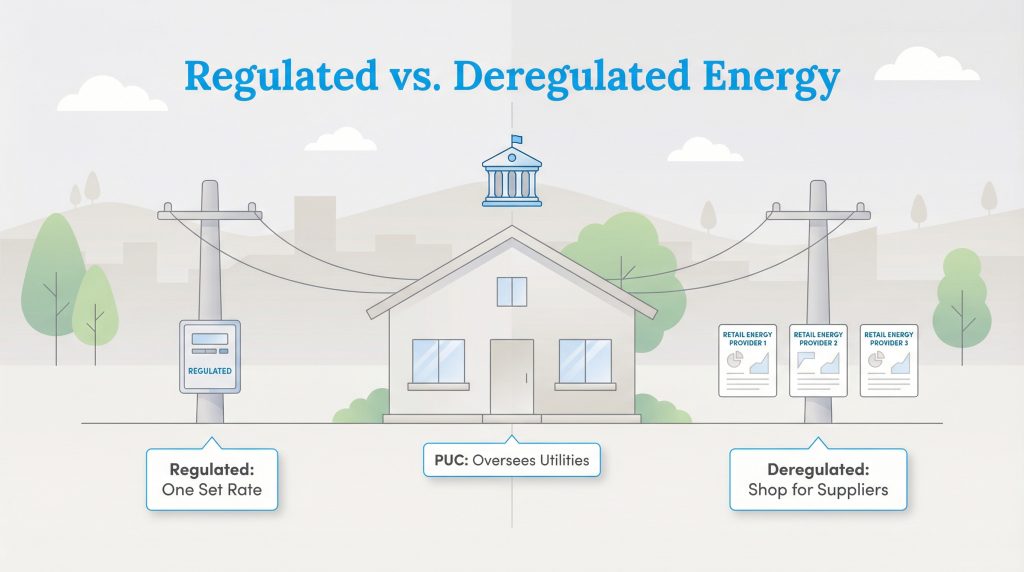
The power a Public Utilities Commission holds over your monthly bill depends heavily on whether you live in a regulated or deregulated energy market. Understanding regulated vs deregulated energy markets is crucial for knowing your rights, your options, and how to save on your electric bill.
In a fully regulated market, your local utility is essentially a monopoly that controls the delivery system, and often the power plants, that serve your home. In this scenario, the PUC sets the exact rate you pay. You generally have only one option for service, and the commission is your only line of defense against price gouging.
In a deregulated market (like parts of Texas, Pennsylvania, and Ohio), the system is split. The PUC still regulates the “delivery” side, the poles, wires, and safety, but the “supply” side is open to competition. Here, independent Retail Energy Providers (REPs) set their own rates for the energy itself. In these states, the PUC monitors the market to prevent fraud and misleading advertising, but they do not set the price per kilowatt-hour for competitive plans.
PUC vs. FERC: Who is Actually in Charge?
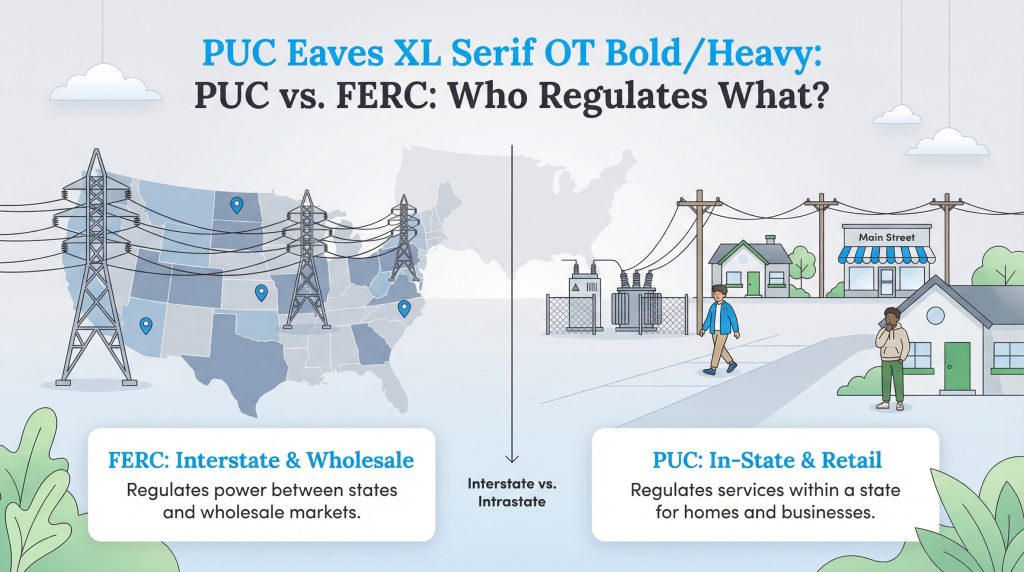
It’s easy to get confused by the alphabet soup of government agencies, especially when trying to distinguish between the Public Utility Commission vs FERC. The distinction comes down to geography and jurisdiction.
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) is a federal agency that regulates the transmission of electricity and natural gas between states (interstate) and oversees wholesale energy markets. They set the rules for the high-voltage highways that move power across the country.
In contrast, the PUC handles issues within the state (intrastate). They regulate the final retail sale of electricity and gas to homeowners and businesses. Think of FERC as the regulator of the wholesale warehouse, while the PUC regulates the retail store where you shop.
The Green Shift: How PUCs Impact Solar and Sustainability
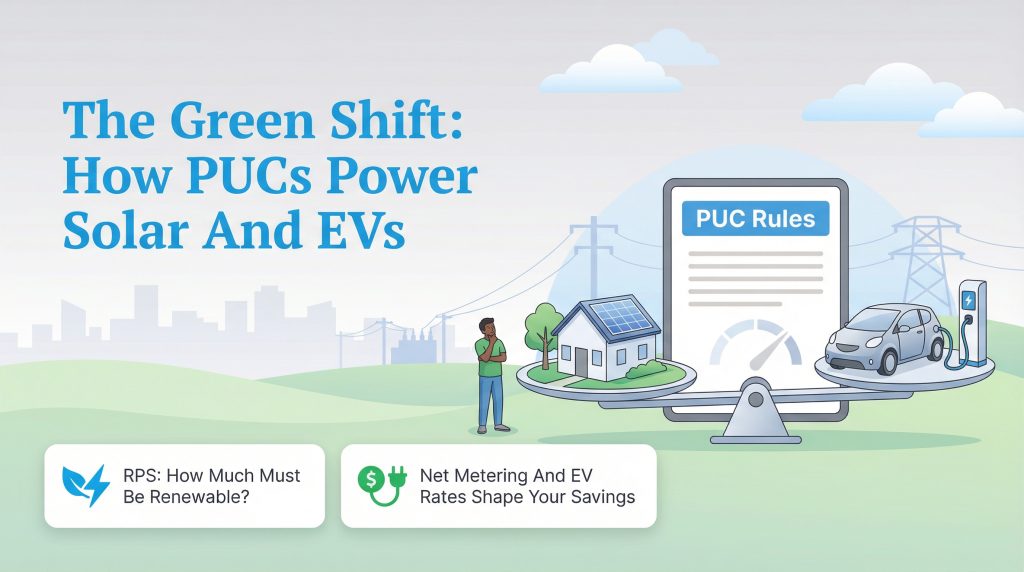
As the grid modernizes, Public Utilities Commissions are playing a pivotal role in the transition to renewable energy. Many states have passed Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS), requiring a certain percentage of power to come from green sources. The PUC is responsible for implementing these rules and ensuring utilities meet their targets.
If you’re considering installing solar panels, the PUC determines your financial return. They set the rules for “Net Metering,” which dictates how much credit you receive on your bill for the excess energy your system sends back to the grid. Furthermore, commissions are currently shaping the future of electric vehicle (EV) adoption by approving investments in charging infrastructure and establishing special time-of-use rates for EV owners.
How to File a Complaint Against a Utility Company

If you are dealing with a persistent issue, such as a billing error, a service refusal, or a failure to refund a deposit, you have the right to escalate the problem. We know how stressful it can be when you feel powerless against a big company, but learning how to file a complaint against utility company providers is a valuable skill for any homeowner. Here is the general PUC complaint process:
- Contact the Utility First: The commission will almost always ask if you have tried to resolve the issue directly with the provider. Call your utility, explain the problem, and ask to speak to a supervisor. Keep a detailed record of who you spoke to, the date, and the outcome.
- Gather Documentation: Before contacting the state, have your account number, recent bills, proof of payment, and your notes from previous calls ready.
- File an Informal Complaint: Visit your state commission’s website to file an informal complaint. This usually triggers a mediation process where the PUC sends your complaint to the utility and demands a response within a set timeframe (often 30 days).
- File a Formal Complaint: If the informal process does not resolve the issue, you can file a formal complaint. This is a legal proceeding that may look like a court hearing, requiring evidence and potentially legal representation.
To find the specific contact information for your state, you can use the directory provided by the National Association of Regulatory Utility Commissioners (NARUC).
How Understanding the PUC Puts You in Control
It’s easy to view the Public Utilities Commission as a distant bureaucratic entity, but it exists to serve you. These commissioners make decisions that directly affect your wallet, your comfort, and your environment. By understanding what they do, you transform from a passive ratepayer into an empowered consumer.
Take the time to review your utility bills, know your rights regarding service shutoffs, and don’t hesitate to utilize the complaint process if you’re being treated unfairly. In deregulated markets, use the tools the commission provides to vote with your wallet by switching to a provider that offers better rates or greener energy. Remember, when you’re setting up utilities in a new home, knowing who regulates your rates is just as important as knowing who sends the bill.
Frequently Asked Questions About Public Utilities Commissions
Is a Public Utilities Commission a government agency?
Can the PUC lower my electric bill?
What is the difference between the PUC and the PSC?
Does the PUC regulate internet and cable providers?
How do I find out who regulates utilities in my state?
About the Author
LaLeesha has a Masters degree in English and enjoys writing whenever she has the chance. She is passionate about gardening, reducing her carbon footprint, and protecting the environment.
