Key Takeaways
- With a fixed rate, you’ll pay the same price per unit of energy throughout your contract, making it easier to budget and protect against market price increases.
- Variable rates can change based on market conditions, which means your energy costs might decrease when prices drop but could also rise if the market spikes.
- Utility rates can be influenced by regulatory changes, market conditions, infrastructure investments, demand shifts, and environmental policies, all of which can cause rates to vary over time.
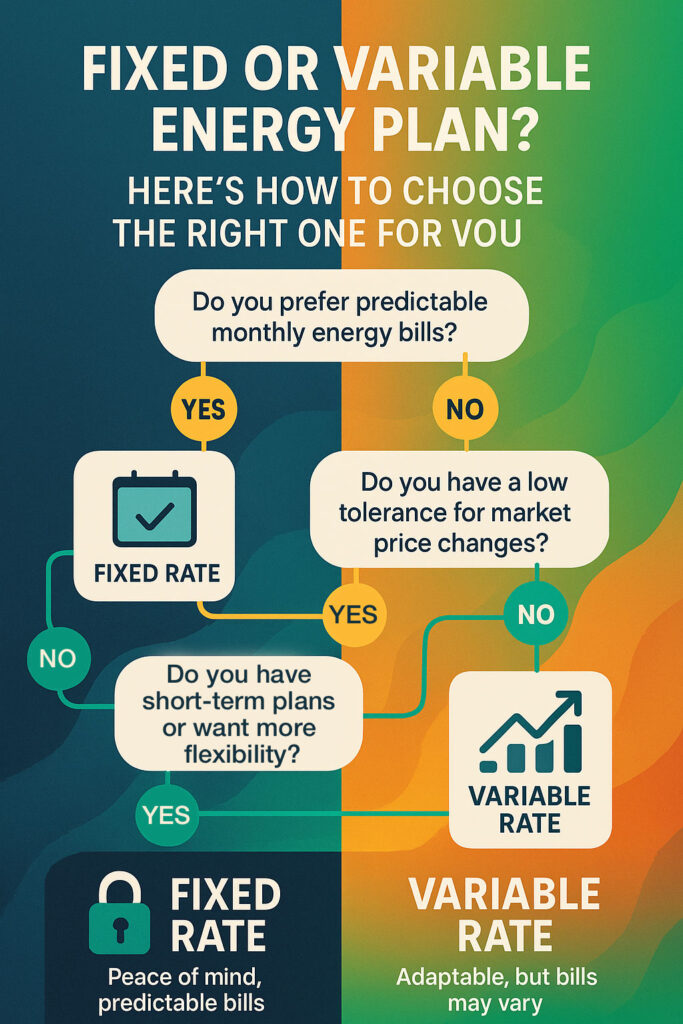
As you are shopping for a new electric or natural gas provider you will notice that some plans have fixed rates, variable rates or even a combination of both. It’s important that you understand the difference and how this can impact your monthly utility bill before entering a contract. Also keep in mind many providers have contracts that are different lengths and that there can be an early termination charge.
What Is a Fixed Rate?
A fixed rate or fixed pricing refers to a price per unit of electricity (kilowatt-hour) or natural gas (therm) that is set and won’t change for a period of time. A fixed rate is a guarantee that your rate will not change during that time even if the market fluctuates.
Pros
- Consistent pricing throughout your contract
- Easier to budget and anticipate your utility bill
- Keep a lower rate even if the market adjusts higher
Cons
- Possible to have a higer rate if the market fluctuates lower
- You likely have less flexibility. Early termination often comes with a fee.
If you’re shopping for a natural gas plan, remember fixed rate plans can help shield you from seasonal spikes in natural gas prices, especially during the high-demand winter months. By locking in your rate during the summer months, you’ll enjoy predictable bills and peace of mind knowing your costs won’t suddenly climb when temperatures drop. This stability makes fixed plans a good choice if you want consistency year-round.
What Is a Variable Rate?
A variable rate or variable pricing allows your rate to adjust upwards and downwards to match any market fluctuations. It is important to understand:
- How often your rate can change. Some providers will adjust on a monthly, weekly or even daily basis.
- What the maximum price you can be charged is or if there is no limit to how high the rate can go. You should be aware if you are protected in the case the market price increases dramatically.
- How does the provider set the rate. Some providers will have a specific formula they use and others may use a non-specific method tied to market price.
Pros:
- Market savings: You might pay less during times of low demand or falling energy prices.
- No long-term commitment: These plans are usually month-to-month with no cancellation fees.
- Good for short stays: Ideal if you’re in a temporary living situation or plan to move soon.
Cons:
- Volatile pricing: Your rate can spike unexpectedly, especially during high demand periods (like winter storms or heatwaves).
- Harder to budget: Monthly bills can be unpredictable.
What Factors Should You Consider in Choosing a Plan?
Choosing between a fixed or variable rate energy plan really comes down to what works best for your lifestyle and comfort level. If you like knowing exactly what to expect on your energy bill each month, a fixed rate plan offers that peace of mind, your rate stays the same no matter what the market’s doing, which makes budgeting a whole lot easier. It’s a great option if you’re planning to stay put for a while and prefer stability. On the flip side, if you’re okay with a little unpredictability and want the chance to save when market prices dip, a variable rate plan might be a better fit. It’s often more flexible and ideal for shorter stays or if you don’t mind keeping an eye on energy trends. Think about your risk tolerance, how long you’ll be in your home, and how hands-on you want to be with your energy plan, those are the real keys to finding the right fit. Consider these items as you choose an energy plan:
- Stability vs. Flexibility: Do you prefer consistent bills, or are you okay with fluctuation for potential savings?
- How long you’ll be in the home: Fixed makes more sense for long-term stays; variable might be better for short-term.
- Risk tolerance: Are you comfortable with market swings, or do you want to avoid surprises?
- Seasonal usage: If you use a lot of energy in high-demand seasons, a fixed rate could shield you from surges.
Why Do Utility Rates Change?
Utility rates change at different frequencies depending on several factors:
- Regulatory Changes: Utility rates are typically subject to regulation by government agencies at the local, state, or national level. Changes in these regulations can lead to adjustments in utility rates. These changes typically occur after regulatory reviews or legislative actions.
- Market Conditions: Fluctuations in energy markets, such as changes in the prices of fuel commodities like natural gas or coal, can impact utility rates. These changes occur very frequently, sometimes even daily, based on market dynamics.
- Infrastructure Investments: Utility companies may need to upgrade or incur maintenance on their infrastructure, such as power plants, transmission lines, or water treatment facilities. These investments can lead to changes in utility rates to cover the costs. These types of increases in utility rates occur infrequently.
- Demand-Side Factors: Changes in consumer demand for utilities, such as during peak usage periods or due to shifts in population or economic activity, can influence utility rates. These changes may result in adjustments to rates to manage supply and demand balance.
- Environmental Policies: Policies aimed at promoting renewable energy sources or reducing carbon emissions can also impact utility rates. For example, mandates for renewable energy targets or carbon pricing mechanisms may lead to changes in utility rates over time.
Utility rates often change seasonally, but they can also change periodically or in response to specific events or conditions, and the frequency of these changes can vary based on a range of factors affecting the utility industry and the broader economy.
FAQs About Fixed & Variable Rate Plans
What is the difference between a fixed-rate and a variable-rate electric plan?
Variable-Rate Plan: The price per kWh can change monthly based on market conditions, energy demand, and other factors. This means your bill can vary significantly from month to month.
Which type of plan is more cost-effective?
Variable-Rate Plan: Can be cheaper if energy prices drop, but it also carries the risk of higher costs if prices increase.
Are there any penalties for switching plans?
Variable-Rate Plan: Typically does not have long-term contracts or early termination fees, offering more flexibility to switch plans or providers.
How do I know which type of plan is right for me?
Variable-Rate Plan: Suitable for those who are comfortable with price fluctuations and may benefit from lower rates when market prices drop.
Can I switch from a fixed-rate to a variable-rate plan (or vice versa)?
What happens when my fixed-rate contract ends?
Are variable-rate plans riskier?
Do fixed-rate plans have any disadvantages?
How do I compare fixed and variable-rate plans?
About the Author
David has been an integral part of some of the biggest utility sites on the internet, including InMyArea.com, HighSpeedInternet.com, BroadbandNow.com, and U.S. News. He brings over 15 years of experience writing about, compiling and analyzing utility data.
